Pulsed, steady or someplace in between? Useful resource dynamics matter within the optimisation of microbial communities
[ad_1]
There’s a rising impetus to leverage our basic understanding of microbial neighborhood meeting in the direction of utilized issues. With microbes contributing to various physiological, biogeochemical, and agricultural processes, the potential to manage and optimise microbial communities holds promise for interventions starting from industrial and environmental remediation to human drugs and biofuel manufacturing [1, 2]. Realising this objective is contingent on excessive constancy between concept, experiments, and the pure dynamics of goal methods.
Theoretical and experimental analysis in microbial neighborhood optimisation has largely proceeded alongside two parallel paths. Theoretical approaches leverage mathematical fashions and metabolic networks to foretell which species mixtures are secure and the way they’ll optimise a given perform (e.g., most biomass, waste degradation or host well being) [3,4,5,6,7]. Experimental research usually take a combinatorial strategy, iteratively assembling completely different species mixtures in vitro and evaluating their stability and practical attributes [8,9,10,11]. Each concept and experiments are priceless however they’re additionally vulnerable to their very own modus operandi that will restrict their correspondence and their translation to real-world methods. On the one hand, theoretical approaches sometimes undertake the analytical tractability of regular state dynamics, the place microbial shoppers and the assets on which they rely are assumed to determine a secure equilibrium. However, experimental approaches virtually completely embrace the high-throughput effectivity of serial-batch tradition, the place shoppers and assets are made to fluctuate over a number of orders of magnitude with every serial passage. This raises an vital query: ought to we anticipate unity within the composition of optimised communities rising beneath steady useful resource provide (e.g., chemostat) versus the discrete pulsed useful resource provide of, for instance, serial-batch tradition?
To discover how microbial neighborhood composition varies beneath contrasting useful resource provide dynamics, we carried out simulations of a classical resource-competition mannequin:
$$frac{{dN_i}}{{dt}} = N_ileft( {mathop {sum}limits_{j = 1}^n {mu _{ij}left( {R_j} proper) – m} } proper)$$
(1)
$$frac{{dR_j}}{{dt}} = {Psi}_jleft( {R_j} proper) – mathop {sum }limits_{i = 1}^n Q_{ij}mu _{ij}left( {R_j} proper)N_i,$$
(2)
the place Ni is the inhabitants density of shopper i, Rj is the focus of useful resource j, μij(Rj) is the per capita practical response of shopper i, m is the per capita mortality fee because of dilution, Ψj(Rj) is the useful resource provide perform, and Qij is the useful resource quota of shopper i on useful resource j (quantity of useful resource per unit shopper). The buyer practical response is given by the Monod perform, (mu _{ij}(R_j) = mu _{max_{ij}}frac{{R_j}}{{K_{s_{ij}} + R_j}}) , the place (mu _{max_{ij}}) is the utmost development fee and (K_{s_{ij}}) is the half saturation fixed for shopper i on useful resource j.
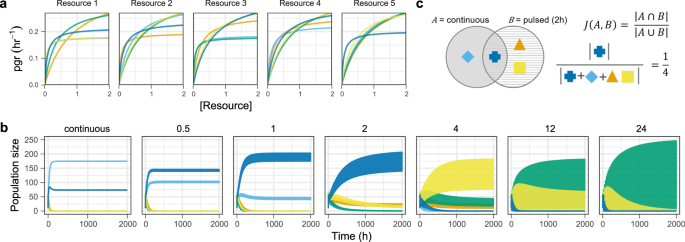
To arrange the simulations, we randomly sampled the parameters of the Monod development features, (μmax and Okays) for 5 species competing for 5 substitutable assets (important assets are handled individually within the supplementary info, with comparable findings). In a single set of parametrisations (n = 100 distinctive competitor mixtures) we used each random μmax and Okays, and in one other set (n = 100) we imposed a trade-off in most development fee and substrate affinity (( {frac{{mu _{max}}}{{K_s}}} )) (Fig. 1a). The rationale for imposing a trade-off is that metabolic concept predicts that organisms that make investments power right into a excessive most development fee may have decrease substrate affinities and vice versa [12, 13]. To make sure cheap development charges relative to the time-scale of useful resource pulsing, we sampled μmax such that minimal doubling instances spanned from 21 to 52 min (when all assets are non-limiting). For every of the random competitor mixtures, we simulated assets beneath steady or pulsed useful resource provide with useful resource replenishment each 1/2, 1, 2, 4, 12, or 24 h. Underneath pulsed useful resource provide, Ψj(Rj) and m are faraway from Eq. (1) and (2) and changed by discontinuous useful resource pulsing and cell switch at mounted intervals. The entire useful resource flux (and mortality) was held fixed beneath all frequencies of useful resource provide i.e., much less frequent replenishment corresponds to bigger useful resource pulses (see Supplementary Data for full mannequin/simulation specs).
a Per capita development responses (Monod features) from a single iteration of the mannequin assuming a trade-off between most development fee and useful resource affinity (colors correspond to particular person shoppers). b Time sequence of shoppers in a beneath completely different useful resource provide regimes. Numbers above particular person panels replicate pulsing intervals in hours. The amplitude of inhabitants fluctuations will increase with longer intervals between pulses, with distinct phases of development, saturation, and instantaneous mortality seen at a finer temporal decision (Fig. S10). c Instance measure of compositional overlap (Jaccard similarity index) between communities assembled beneath steady useful resource provide (far left panel in b) vs. pulsing each two hours (centre panel in b).
After permitting the rivals to succeed in a gradual state (time-averaged over 24 h beneath pulsed therapies), we quantified the correspondence between the continual provide remedy and the pulsed therapies utilizing the Jaccard similarity index, (Jleft( {A,B} proper) = frac{{left| {A cap B} proper|}}{{left| {A cup B} proper|}}) (0 ≤ J(A,B) ≤ 1), the place the numerator provides the variety of species (max = 5) that persist beneath steady (A) and pulsed (B) useful resource provide, and the denominator provides the variety of species (max = 5) that persist beneath steady or pulsed useful resource provide (Fig. 1b, c).
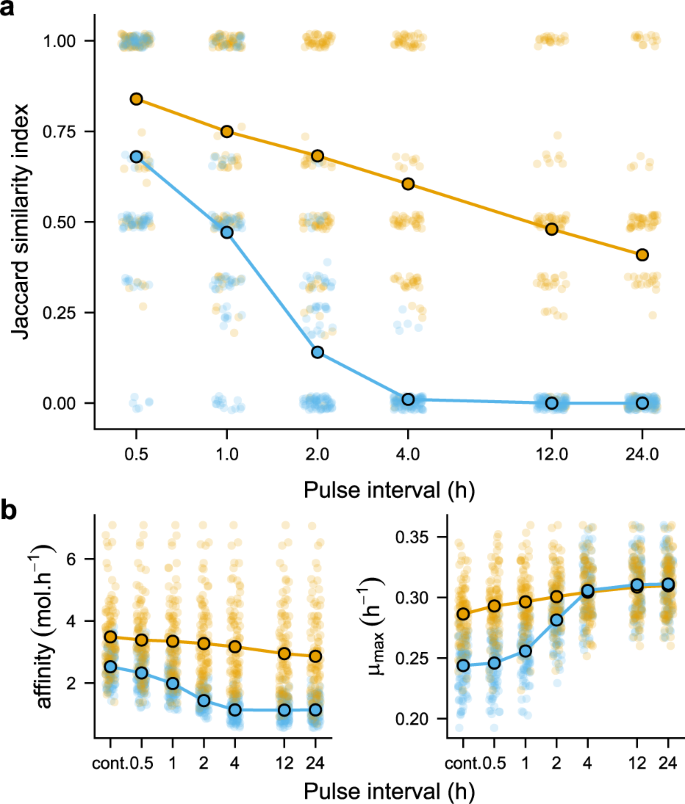
Underneath each units of simulations (with and with out implementing a trade-off between maximal development fee and useful resource affinity), we observe that the similarity in closing neighborhood composition between steady and pulsed useful resource provide decays with more and more massive intervals between useful resource replenishment (Fig. 2a). When no trade-off is imposed between most development fee and useful resource affinity (orange line in Fig. 2a) the imply compositional similarity is simply 0.68 when assets are pulsed each 2 h and right down to 0.41 when assets are pulsed each 24 h (typical of serial-batch tradition). The speed of decay within the Jaccard index is extra extreme when a trade-off is imposed between most development fee and substrate affinity, to the extent that when pulsing intervals attain 4 hours there may be virtually zero overlap in neighborhood composition (blue line in Fig. 2a).
a Compositional overlap (Jaccard similarity) between communities beneath steady versus pulsed useful resource provide. Orange traces, factors and circles denote mannequin parametrisations with random sampling of each μmax and Okays; blue traces, factors and circles denote mannequin parametrisations with a trade-off imposed between μmax and useful resource affinity (( {frac{{mu _{max}}}{{K_s}}} )). Simulation parameters offered within the Supplementary Data. b Imply trait values for affinity and μmax averaged for every shopper throughout the 5 assets and weighted by their closing abundance on the finish of a simulation (cont. = steady). In each a and b, small factors (jittered for readability) give the results of a person simulation; massive circles point out the corresponding imply.
Ecological concept supplies an intuitive clarification for these observations. When assets are extra repeatedly equipped, the higher competitor is the one that may maintain a optimistic development fee on the lowest concentrations of a limiting useful resource (i.e., has a better useful resource affinity or decrease R* within the language of useful resource competitors concept [14]). In distinction, beneath more and more pulsed useful resource provide, the higher competitor is the one that may develop quickly at greater useful resource concentrations. Having a excessive useful resource affinity (low R*) is of little profit if useful resource concentrations fluctuate over massive amplitudes as a result of it solely confers an ephemeral aggressive benefit within the transient interval earlier than the useful resource is totally depleted (forward of the following useful resource pulse). As a substitute, a excessive most development fee is perfect as a result of it permits the patron to develop quickly and shortly deplete a shared limiting useful resource. This excessive most development technique is, nevertheless, sub-optimal beneath steady useful resource provide as a result of a low R* strategist can draw the useful resource down and maintain it at a focus at which the utmost development strategist is unable to take care of a optimistic development fee.
Wanting on the imply trait values for useful resource affinity and μmax weighted by every shopper’s closing abundance, it’s certainly obvious that buyers with a better affinity (averaged throughout the 5 assets) are favoured beneath steady useful resource provide, whereas shoppers with excessive most development charges are favoured beneath pulsing intervals of accelerating size (Fig. 2b). Imposing this trade-off, due to this fact, results in the fast decline in compositional similarity we observe beneath useful resource pulsing. Notably, it additionally results in a richness peak at intermediate pulsing intervals, the place these different methods have a better chance of coexisting [15] (Fig. S1). On the identical time, we nonetheless observe a decline in compositional similarity when μmax and Okays are randomly sampled independently of one another just because the trade-off between most development and useful resource affinity will emerge sometimes by probability. Two experimental assessments of microbial neighborhood composition beneath steady versus pulsed useful resource provide are in keeping with these observations [16, 17].
To guage the sensitivity of those observations to completely different assumptions, we ran further simulations beneath varied different mannequin parameterisations and formulations. In short, comparable tendencies to these described above are noticed when: i) most development charges are quicker or slower than these offered in the principle textual content (Figs. S2, S3); ii) all assets are assumed to be important to development (following Liebig’s legislation of the minimal) (Fig. S4); iii) a weaker trade-off is imposed between most development and affinity (Figs. S5, S6); or iv) mortality is steady moderately than intermittent (Figs. S7, S8). We additionally investigated the connection between noticed compositional overlap and the dynamical stability beneath steady useful resource provide, anticipating that extra secure communities would are usually extra proof against compositional shifts beneath useful resource pulsing. The truth seems extra nuanced, specifically that weaker dynamical stability on the restrict of fixed useful resource provide is related to greater variance in compositional overlap beneath steady vs. pulsed circumstances (Fig. S9). In different phrases, methods with weaker stability are much less predictable. A variety of different microbial traits and trade-offs could work together unpredictably with the connection between useful resource provide and neighborhood composition. The potential modulating position of system instabilities generated by cross-feeding interactions, non-convex trade-off features, and the evolution of specialist versus generalist methods current a number of particularly priceless traces of enquiry [18,19,20].
Though these observations are germane to any consumer-resource system, our emphasis right here is on the rising area of microbial neighborhood optimisation, the place the sensible implications are particularly well timed and vital; specifically, the useful resource provide regime should be tailor-made to the neighborhood being optimised. For instance, wastewater remedy is likely to be extra appropriately modelled beneath steady useful resource provide [21], whereas fermented meals and beverage manufacturing could also be extra carefully allied to the pulsed useful resource dynamics noticed in batch tradition [22]. Useful resource provide may also be manipulated to favourably modify the aggressive hierarchy in an present neighborhood (e.g., by regulating the speed of nutrient provide to the intestine by meal timing). Certainly, there may be rising proof that feeding frequency can drive vital modifications in intestine microbiota composition [23, 24]. Thus, useful resource provide dynamics ought to be thought-about each a constraint within the design of novel microbial communities and as a tuning mechanism for the optimisation of preexisting communities like these discovered within the human intestine.
[ad_2]
Source_link