Magnetic NH2-MIL-101(Al)/Chitosan nanocomposite as a novel adsorbent for the elimination of azithromycin: modeling and course of optimization
[ad_1]
Adsorbent traits
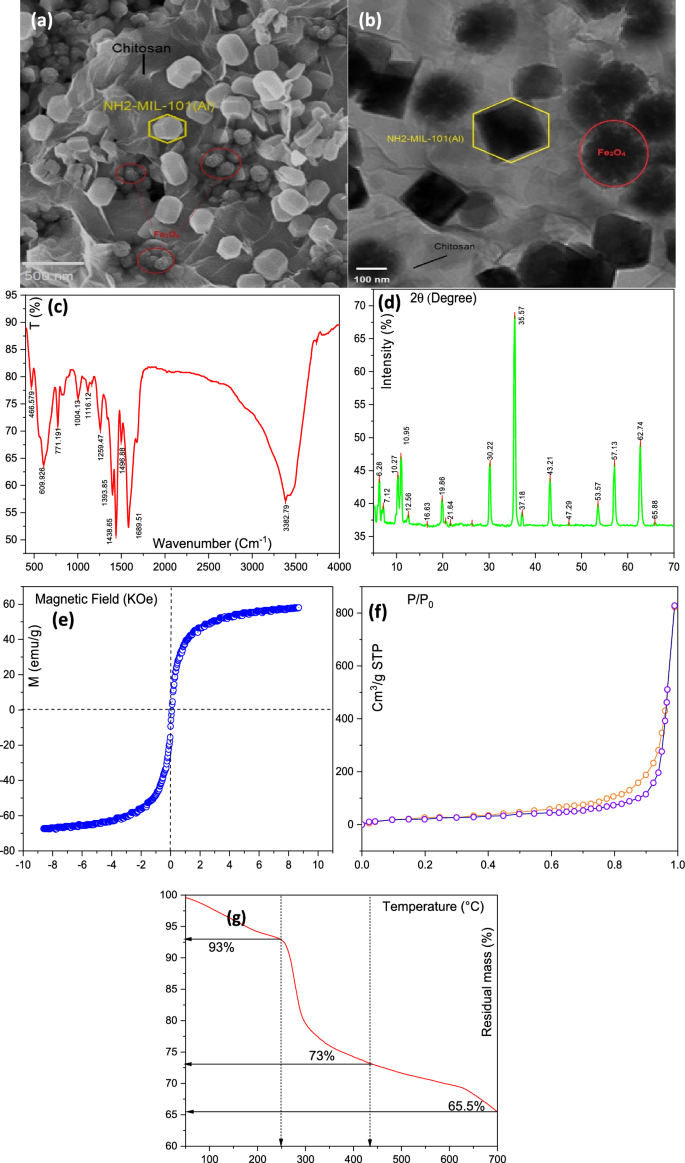
The SEM evaluation of the MIL/Cs@Fe3O4 NCs is proven in Fig. 1a. As proven, NH2-MILAl-101 with hexagonal form and common diameter of 88.5 ± 10.1 nm are distributed non-uniformly on the floor of chitosan. The floor of chitosan is noticed as clean, sheet-like and layered type. In different sides, Fe3O4 NPs with spherical construction (23.3 ± 4.0 nm) are observable on the chitosan floor. The picture reveals that the floor of the adsorbent is tough and has porosity. This characteristic results in a greater contact of the adsorbent with the pollutant, which resulted in an enchancment in adsorption efficiency. Moreover, no agglomeration is seen within the MIL/Cs@Fe3O4 NCs construction which may be associated to the presence of chitosan within the construction of the synthesized pattern. A TEM evaluation was utilized to analyze the form and particle sizes of MIL/Cs@Fe3O4 NCs, and its outcomes are offered in Fig. 1b. The pictures point out that the NH2-MILAl-101 and Fe3O4 nanoparticles are hexagonal and spherical respectively and distributed heterogeneously in a measurement vary of 80–100 nm and 20–40 nm on the chitosan floor, which coincides with outcomes obtained from SEM picture. As a result of increased density of NH2-MILAl-101 and Fe3O4 than chitosan, these nanoparticles are acknowledged in a darker coloration (black), whereas chitosan has a lightweight and clear construction. DLS method was employed to find out the particle measurement distribution (Determine will not be proven): the obtained common sizes of Fe3O4 NPs, NH2-MILAl-101 and MIL/Cs@Fe3O4 NCs had been 21.75 nm, 85.34 nm and 108.96 nm, respectively. The FTIR spectrum of the adsorbents at a wavelength inside 400–4000 cm−1 is proven in Fig. 1c. The height at 609 cm−1 is attributed to the Fe–O vibration of Fe3O4 NPs31. The medium peak at 466 cm−1 is because of Al–O vibrations, which confirms the formation of the organometallic construction. The broad peak from 3382 cm−1 is attributed to the –NH2 and –OH teams and the peaks at 1689 and 1598 cm−1 are associated to the CONH2 and NH2 teams within the chitosan construction, respectively32. The peaks at 1438 and 1496 cm−1 had been assigned to symmetric and uneven stretching of carboxyl teams, respectively. The height at 1393 and 771 cm−1 correspond to the –COO– bond and C–H vibration of the fragrant cycles within the phenyl ring. These bonds at 1438, 1496, 1393 and 771 cm−1 recommend the presence of the natural ligands of 2-aminoterephthalic acid. Two peaks showing at 1259 and 1116 cm−1 may be attributed to the stretching vibrations of fragrant practical epoxy C–O and alkoxy C–O teams, respectively. XRD sample of synthesised MIL/Cs@Fe3O4 NCs within the vary of 2θ = 5–70° is represented in Fig. 1d. The attribute peaks of NH2-MILAl-101 are appeared at 2θ = 6.28°, 7.12°, 8.89°, 10.27° and 17°, which had been comparatively just like the patterns of earlier references33,34. The diffraction peaks at 10.96°, 19.86° and 21.64° are assigned to crystal types of chitosan. However, the obtained peaks at 26.3°, 30.22°, 35.57°, 43.21°, 53.57°, 62.74°, and 65.88° associated to the diffraction planes of 172°, 220°, 342°, 400°, 511°, 122°, and 106°, respectively verify the presence of Fe3O4 crystals within the MIL/Cs@Fe3O4 NCs construction (0866-088-01 JCPDS NO.). The above outcomes point out that NH2-MILAl-101 and Fe3O4 NPs are loaded onto the CS and MIL/Cs@Fe3O4 NCs was synthesized efficiently. Magnetic measurements and separation of MIL/Cs@Fe3O4 NCs had been taken with a VSM evaluation at room temperature, as offered in Fig. 1e. This evaluation was carried out in a magnetic subject of ± 10 KOe and saturation magnetization round ± 80 emu/g. The outcomes confirmed that the saturation magnetization (Ms) of MIL/Cs@Fe3O4 NCs was noticed round 60.77 emu/g. The outcome clearly demonstrated the suitable magnetic property of the synthesized adsorbent. The Nitrogen adsorption–desorption isotherms and the pore measurement distribution of the MIL/Cs@Fe3O4 NCs is proven in Fig. 1f and Supplementary Desk S1. The isotherms are recognized as kind IV with H4 typical hysteresis loops, that are the attribute isotherm of mesoporous supplies in accordance with IUPAC classification. The BET floor space and common pore diameters of the of the product had been additionally calculated as 451.73 m2/g and a pair of.78 nm, respectively. The BET floor space calculated for the MIL/Cs@Fe3O4 NCs is ~ 1.5 occasions increased than the Fe3O4@C nanocomposite synthesized by Van Tran et al.35. Though these values are increased than all samples (Fe3O4 NPs, NH2-MILAl-101 and MIL/Cs NCs), however this distinction between MIL/Cs@Fe3O4 NCs and MIL/Cs NCs will not be too massive. This phenomenon could also be as a result of occupation of the porosity of MIL/Cs NCs by magnetic nanoparticles (Fe3O4) and/or clotting (agglomeration) of the nanocomposite. Thermal stabilities of MIL/Cs@Fe3O4 NCs had been investigated by utilizing TGA evaluation (Fig. 1g). MIL/Cs@Fe3O4 NCs confirmed gradual weight reduction inside three steps. Step one occurred within the temperature vary of fifty–250 °C with a weight lack of 7%, attributed to the evaporation of solvent or water molecules contained in the framework. A weight lack of 20% within the temperature vary of 150–440 °C could possibly be ascribed to the decomposition of visitor molecules or unreacted merchandise contained in the ligand construction. Within the remaining step, past 440 °C, MIL/Cs@Fe3O4 NCs construction degraded. The thermal stability outcomes revealed the great stability of the synthesized adsorbent.
AZT elimination beneath completely different programs
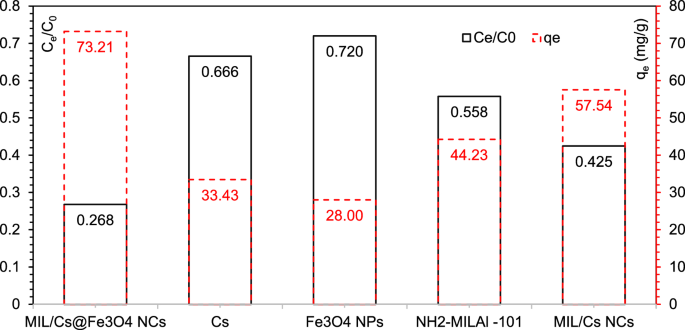
Determine 2 reveals the flexibility of MIL/Cs@Fe3O4 NCs in comparison with Cs, Fe3O4, NH2-MILAl-101 and MIL/Cs NCs for AZT elimination beneath related experimental circumstances (experiment circumstances: Contact time: 60 min, pH: 7 ± 0.4, Pattern dose: 0.5 g/L, AZT Conc.: 50 mg/L). AZT elimination efficiencies by Cs and Fe3O4 had been negligible (33.43 and 28%, respectively), exhibiting that AZT can’t be successfully eliminated by Cs and Fe3O4. Nevertheless, increased elimination efficiencies had been noticed when Cs and Fe3O4 had been coupled with NH2-MILAl-101 i.e., MIL/Cs NCs and MIL/Cs@Fe3O4 NCs. The elimination efficiencies of AZT by NH2-MILAl-101, MIL/Cs NCs and MIL/Cs@Fe3O4 NCs had been 44.23, 57.54 and 73.21% inside 60 min, respectively. Increased floor space, higher common pore quantity/ measurement and extra practical teams appear to be the explanations for the superior efficiency of MIL/Cs@Fe3O4 NCs over different adsorbents. The precedence and order of samples in AZT elimination had been obtained as MIL/Cs@Fe3O4 NCs > MIL/Cs NCs > NH2-MILAl-101 > Cs > Fe3O4, respectively. Accordingly, MIL/Cs@Fe3O4 NCs was chosen as the popular adsorbent in AZT elimination and was utilized in following experiments.
Impact of key parameters on adsorption of AZT
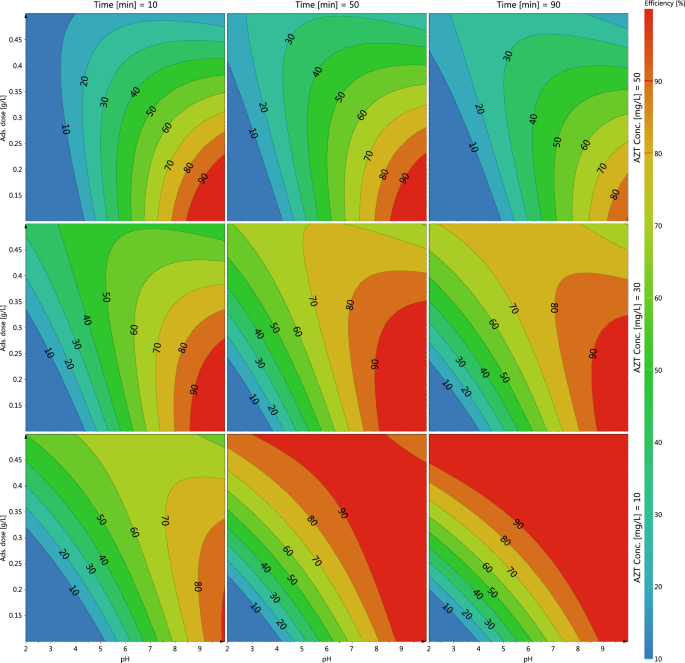
The impact of pH adjustments within the vary of two to 10 on AZT adsorption by MIL/Cs@Fe3O4 NCs was investigated. As may be seen from Fig. 3, the elimination effectivity is improved by rising the pH in order that the very best effectivity is noticed in alkaline circumstances and the bottom was obtained at pH < 5. In different aspect, the purpose of zero cost (pHpzc) values for MIL/Cs@Fe3O4 NCs was obtained to be 4.6 (Supplementary Fig. S1). The rising development of AZT elimination with rising the pH of the answer may be related to the truth that pHpzc (4.6) of adsorbent is decrease than the pKa (8.7) of AZT (pHpzc < pH < pKa). Due to this fact, at pH = ~ 8, the floor fees of the adsorbent and the adsorbate change into opposites cost and an electrostatic attraction happens between them which leads to most adsorption. In consequence, the optimum pH 8 was employed in additional adsorption assessments. Imani poor et al. (2021) studied the adsorption of azithromycin onto L-methionine modified montmorillonite K10 and 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane functionalized magnesium phyllosilicate organoclays. They discovered that the utmost adsorption capability obtained at a pH 8.0 ± 0.136. An analogous outcome was noticed for azithromycin elimination utilizing powdered zeolites in analysis by Sousa et al.37. They reported that the bottom effectivity was recorded beneath acidic pH (2.5–4.5), whereas alkaline circumstances improved the efficiency of the azithromycin adsorption course of. The consequences of adsorbent dosage (from 0.1 to 0.5 g/L) on adsorption of AZT by MIL/Cs@Fe3O4 NCs was investigated at pH = 8.0, contact time = 60 min, and room temperature. Based mostly on the outcomes, the rise within the adsorbent dose has led to a rise in adsorption effectivity from 53 to 76%. The particular floor space and huge amount of reactive floor facilities or practical teams of the adsorbent in direction of contaminates could be related to adsorption share enchancment as adsorbent will increase38,39. Wahab et al. discovered that rising the quantity of magnetic activated carbon (MAC) from 0.01 to 0.15 g can improve the elimination effectivity of AZT from ~ 10 to 100%40. In azithromycin adsorption onto modified pure clinoptilolite, Saadi et al. noticed a direct relationship between course of effectiveness and adsorbent dose. They reported that the preliminary fast adsorption was attributed to the unoccupied web site and floor space of absorbent, leading to profitable adsorbate diffusion inside the adsorbent41. The adsorption of AZT on MIL/Cs@Fe3O4 NCs was studied by adjusting contact time within the optimized pH and adsorbent dosage. From Fig. 3, rising the contact time from 10 to 90 min has resulted in a 20% enchancment in effectivity. Effectivity enhancements with rising time may be as a result of improve the contact and collisions of AZT with the MIL/Cs@Fe3O4 NCs, which subsequently improves the mass switch of contaminates on to the adsorbent. Adsorbents usually have a restricted and particular adsorption capability and change into saturated after reaching equilibrium time. The correct effectivity originally of the adsorption course of may be linked to the existence of huge unoccupied websites and practical teams on the adsorbents that start to fill over time42. A extra detailed concerning the impact of contact time on azithromycin adsorption has been mentioned and reported within the kinetics research part. Balarak et al. investigated the impact of contact time on AZT molecule adsorption on Azolla Filiculoides-based activated porous carbon starting from 0 to 150 min. They discovered that rising the contact time results in a rise in share elimination43. Different researchers have noticed related leads to the adsorption of various antibiotics by modified alpha alumina nanoparticles and NaY zeolite synthesized from wheat straws ash44,45. Growing the preliminary concentrations from 10 to 50 mg/L has resulted in a substantial drop in effectivity, as seen in Fig. 3. The inverse relationship between AZT focus and effectivity is owed to the saturation of accessible lively websites on MIL/Cs@Fe3O4 NCs. Quite the opposite, rising the preliminary focus of AZT has led to a rise in adsorbate per mass of adsorbent (qe, mg/g). The elevated in qe (mg/g) at increased concentrations could be defined by the numerous driving power for mass trade at a big preliminary focus46. Davoodi et al. studied the elimination of AZT utilizing uncooked and saponin-modified nano diatomite by various the preliminary AZM focus from 20 to 100 mg/L. They seen that rising the pollutant focus causes a big discount within the adsorption course of47. In 2020, Ardakani et al. used from PECVD movie to guage the affect of preliminary focus on AZT elimination48. In accordance with the Ardakani report’s, rising the AZT focus from 0 to 160 mg/L has resulted in a lower in effectivity, and the very best effectivity has been obtained within the lowest focus. Fast saturation of lively websites with rising pollutant focus was the principle explanation for effectivity discount.
Statistical evaluation and modeling of AZT adsorption
The validity of the mannequin and operational parameters was investigated by RSM-CCD method and ANOVA evaluation. Desk 2 summarizes the ANOVA outcomes for the chosen mannequin. The developed mannequin can nicely describe and predicted the adsorption of AZT by MIL/Cs@Fe3O4 NCs, as evidenced by the excessive values of R2 (> 0.997), Adj R2 (> 0.991), and Mannequin F-value (170.46). Moreover, the R2 worth has moderately agreed with the Adjusted R2 worth; i.e., the distinction is lesser than 0.2. However, RSD (1.873) confirms the mannequin’s suitability for decoding the studied course of. The signal-to-noise ratio is expressed by the sufficient precision (A–P) parameter. This worth was discovered to be 46.973 (A–P > 4) which signifies an sufficient sign and mannequin could possibly be used to navigate the design (good match between experimental and computed outcomes)49. The p-value of the shortage of match parameter was 6.2431e−01 (higher than 0.05), indicating that the developed mannequin was acceptable and the expected values are correct50. Variance evaluation was additionally used to analyze the results of variables. The outcomes present that each one parameters had a substantial affect on the AZT adsorption besides interplay between pH and time, pH and AZT focus and adsorbent dose and time. The equation when it comes to precise elements can be utilized to make predictions concerning the response for given ranges of every issue. The equation of AZT adsorption on MIL/Cs@Fe3O4 NCs may be outlined as follows:
$$mathrm{Effectivity }(mathrm{%}) = 72.56 + 18.59(mathrm{pH}) + 4.11(mathrm{Advertisements}.mathrm{ dose}) +3.82 (mathrm{Time}) -16.26 (mathrm{AZT Conc}.) -9.31 (mathrm{pH}occasions mathrm{Advertisements}.mathrm{ dose}) -1.11(mathrm{pH}occasions mathrm{Time}) +0.963(mathrm{pH}occasions mathrm{ AZT Conc}.) +1.49 (mathrm{Advertisements}.mathrm{ dose}occasions mathrm{ Time}) -8.40 (mathrm{Advertisements}.mathrm{ dose}occasions mathrm{ AZT Conc}.) -4.49 (mathrm{Time}occasions mathrm{ AZT Conc}.) -2.89 {(mathrm{pH})}^{2} -2.61{(mathrm{Advertisements}.mathrm{ dose})} -2.12 {(mathrm{Time})}-8.19 {(mathrm{AZT Conc}.)}^{2}$$
(3)
It may be seen that the (mathrm{pH}), (mathrm{Advertisements}.mathrm{ dose}), (mathrm{Time}), (mathrm{pH}occasions mathrm{ AZT Conc}.) and (mathrm{Advertisements}.mathrm{ dose}occasions mathrm{ Time}) parameters have optimistic indicators, and the others are damaging. These findings present that rising the talked about elements has a synergistic impact on the adsorption course of; nonetheless, rising different parameters reduces the effectivity. In accordance with Eq. (3) and Desk 2, pH with the very best coefficient has the best influence on the AZT adsorption course of by MIL/Cs@Fe3O4 NCs. Plotting precise knowledge Vs. predicted knowledge with R2 > 0.948 illustrated that the developed mannequin has a robust capability to foretell elimination effectivity (Supplementary Fig. S2a). The traditional chance plot of the studentized residuals (Supplementary Fig. S2b), reveals that the plotted factors are near a straight line (balanced and uniform distribution of residuals across the normalcy line.) that signifies the mannequin has been nicely fitted with the experimental outcomes. Supplementary Fig. S2c reveals the residuals are randomly scattered close to the horizontal zero reference (± 3) indicating match of the mannequin for AZT adsorption by MIL/Cs@Fe3O4 NCs.
Course of optimization
After dedication of the impact of every parameter (optimistic and damaging roles) on the adsorption course of, calculating the optimum circumstances is crucial and inevitable51. The aim of optimization was enchancment of AZT adsorption effectivity within the batch course of, so the response parameter (AZT adsorption effectivity) was set to most stage to find out the most effective efficiency of system. The decrease and higher restrict values of different variables had been taken from the experimental knowledge ranges (see Desk 1). Based mostly on the DF method outcomes, the utmost adsorption effectivity for AZT was 98.362 ± 3.24% at pH = 7.992, AZT conc. = 10.107 mg/L, adverts. dose g/L = 0.279 and time equal to 64.256 min. To find out the accuracy of the software program mannequin outcomes, optimized circumstances (the above outcome) had been simulated in laboratory scale and repeated 5 occasions. The proof instructed that the simulated take a look at outcomes (96.021 ± 4.23%) are in keeping with the mannequin’s outcomes (98.362 ± 3.24%), so the outcome recorded by DF was used had been used within the isotherms, kinetics and thermodynamic investigation. The share of parameters participation in maximizing the AZT adsorption course of additionally revealed that pH and time with 64.063 and 1.206%, had the very best and lowest influence on system optimization, respectively.
Adsorption isotherms
To find out the best-fitting isotherm mannequin with experimental knowledge, the Langmuir, Freundlich, Temkin, and Dobbin-Radoshkvich fashions had been studied (circumstances: pH = 7.992, AZT Conc. = 10.107 mg/L, Advertisements. dose g/L = 0.279). From Desk 3 and Supplementary knowledge, Fig. S3, The R2 worth for the Langmuir isotherm (R2 > 0.9981) is increased than different fashions (0.9759, 0.9396, and 0.7093 for Freundlich, Temkin, and Dobbin-Radoshkvich, respectively), indicating that experimental knowledge is in nicely settlement with Langmuir mannequin. The decrease worth of χ2 error (0.011) additionally confirms the outcomes obtained. In accordance with the Langmuir mannequin, the AZT is adsorbed in a monolayer on a homogeneous floor of adsorbent with uniform energies for all of the binding websites with none interplay between the molecules52,53. The adsorption capability upon the Langmuir mannequin was obtained as 238.5527 mg of AZT per gram of MIL/Cs@Fe3O4 NCs. The dimensionless separation issue (RL) of the Langmuir adsorption isotherm was used to find out the favourability of the adsorption course of (irreversible → RL = 0, beneficial → 0 < RL < 1, linear → RL = 1 and unfavourable → RL > 1). All of the RL values lie within the vary of 0 < RL < 1, which means that the AZT are favourably adsorbed on MIL/Cs@Fe3O4 NCs. In comparison with Langmuir isotherm mannequin, Freundlich isotherm mannequin had the poorest match with experimental knowledge, as decided by comparability of R2 and χ2 values. Nevertheless, excessive values of okF (60.837 L mg-1) and n parameter (higher than 1) indicated that adsorption of adsorbate on adsorbent was acceptable/possible54,55. Desk 3 reveals that the experimental knowledge are much less in keeping with the Temkin isotherm mannequin than both of the earlier two fashions. However, the positivity of Temkin isotherm constants (B = 32.042) proves that the adsorption course of within the current research is endothermic in nature. The outcomes indicated that experimental knowledge fitted with the D–R isotherm with R2 > 0.709 beneath the optimized situation. Magnitude of adsorption vitality, E, for AZT adsorption on the MIL/Cs@Fe3O4 NCs adsorbent was calculated to be 2704.0065 kJ/mol (> 40 kJ/mol), representing that the adsorption is chemisorption course of56,57. Non-linear outcomes of the studied isotherms (Fig. S3e) additionally clearly confirmed compliance of the experimental knowledge with the Langmuir isotherm.
Adsorption kinetics
As may be seen from the Supplementary knowledge, Fig. S4e, the adsorption effectivity elevated sharply on the preliminary 60 min of the experiment, whereas negligible adjustments had been noticed thereafter, which signifies that the adsorption course of has reached equilibrium state. The excessive adsorption charge originally of course of could also be defined by the excessive affinity of MIL/Cs@Fe3O4 NCs for trapping pollution as a result of big variety of vacant websites (lively websites) on adsorbent. Over time, the lively websites within the adsorbent construction are occupied (crammed) by pollutant molecules, which leads to diminished effectivity and charge of AZT adsorption58,59. Within the following, 4 typical kinetic fashions together with pseudo-first-order, pseudo-second-order, Elovich, and intraparticle diffusion, had been employed to analyze the kinetics of AZT adsorption on MIL/Cs@Fe3O4 NCs beneath optimized circumstances (see Supplementary knowledge, Fig. S4a–d). Moreover, the parameters associated to the kinetic fashions i.e., error capabilities, and regression correlation coefficients (R2), are listed in Desk 3. A pseudo-first-order mannequin was discovered to be in good settlement with experimental knowledge with a excessive R2 > 0.983, and χ2 values lower than 0.032. Increased R2 values (0.9991) and decrease χ2 charge (0.013) on the one hand and extra compatibility between experimental qe (qe,exp: 35.86 mg/g) with the calculated qe (qe,cal: 37.60 mg/g) then again clearly indicated that the pseudo-second-order mannequin higher describe the adsorption behaviour of AZT onto MIL/Cs@Fe3O4 NCs. The error values (χ2 = 0.039) and R2 parameter (0.9543) obtained from the Elovich mannequin point out that there’s the least settlement between the experimental knowledge and this mannequin, and Elovich mannequin will not be appropriate for describing the experimental knowledge in comparison with the earlier two fashions. The outcomes obtained to date confirmed that the dominant mechanism of adsorption course of is chemisorption60. The outcomes additionally depicted that intraparticle diffusion mannequin with R2 > 0.997 and χ2 = 0.024 has a better capability than pseudo-first-order and Elovich fashions in decoding knowledge, whereas it has a weaker efficiency than pseudo-second-order kinetic mannequin. Apart from, the ensuing becoming line within the intraparticle diffusion plot (qt towards t0.5) didn’t go by means of the origin. This reveals that intraparticle diffusion was a rate-controlling step (rate-limiting mechanism) within the AZT adsorption course of, together with the chemisorption response61,62.
Adsorption thermodynamic
Supplementary knowledge, Fig. S5a reveals the impact of various temperatures on the AZT adsorption effectivity on the obtained optimized circumstances. Because it seems, with rising temperature from 278 to 343 °Okay, adsorption capacities improved from 32.68 to 36.18 mg/g. For evaluating feasibility and nature of AZT adsorption course of on MIL/Cs@Fe3O4 NCs, the thermodynamic parameters i.e., Gibbs free vitality (ΔG°), enthalpy change (ΔH°), and entropy change (ΔS°) had been investigated ant their outcomes are given in Desk 3. The portions of enthalpy and entropy had been calculated from slope and intercept of the plot of ln ln Okayd vs. 1/T (Van’t Hoff plot, Supplementary knowledge, Fig. S5b). The values of ΔH° and ΔS° had been discovered to be 755.23 and 0.22 kJ/mol, respectively. Optimistic worth of ΔH° and in addition the directed development between ln Okayd and temperature implied that AZT adsorption on the MIL/Cs@Fe3O4 NCs was endothermic in nature, indicating that increased temperature enhanced adsorption capability. ΔS° worth grew to become optimistic, so the elevated randomness may be anticipated on the stable/answer interface throughout AZT adsorption. Apart from, optimistic ΔS° worth corresponded to a rise within the freedom diploma of the adsorbed species63. Destructive values of ΔG° (− 8.08 to − 22.85 kJ/mol) indicated feasibility and spontaneous nature of adsorption course of. Furthermore, the diploma of spontaneity was elevated by rising temperature.
Impact of background ions
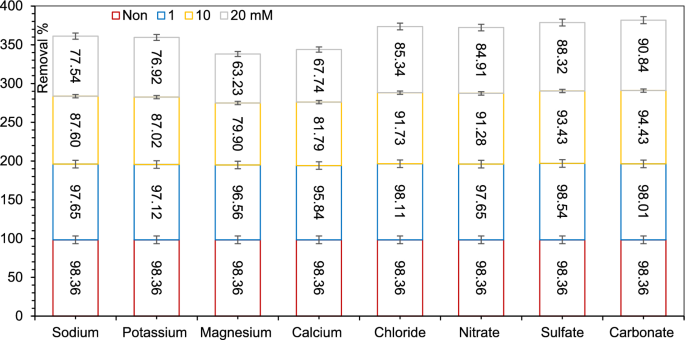
The impact of background electrolytes at an preliminary focus of 1, 10 and 20 mM on AZT adsorption by MIL/Cs@Fe3O4 NCs are proven Fig. 4. It was discovered that the Na+ and Okay+ cations had a smaller impact on antibiotic adsorption than Mg2+ and Ca2+ ions. This could be defined by the truth that the excessive polarization energy of divalent ions precipitated them to exert a stronger squeezing-out impact. The next causes are additionally given by the researchers: (a) A dense water hydration shell may encompass the adsorbed Mg2+ and Ca2+ ions may hinder the accessible adsorption websites by blocking the hydrophobic adsorption area, and (b) It’s doable that Mg2+ and Ca2 compete instantly for adsorption websites on MIL/Cs@Fe3O4 NCs as a result of inner-sphere complexation, which inhibits the formation of charge-assisted H-bonds with antibiotics. AZT adsorption by MIL/Cs@Fe3O4 NCs was not considerably affected by background anions, together with Cl−, NO3−, SO42− and CO32−, which can be as a result of robust repellence/repulsion between anions and the negatively charged adsorbent floor64.
Desorption and stability
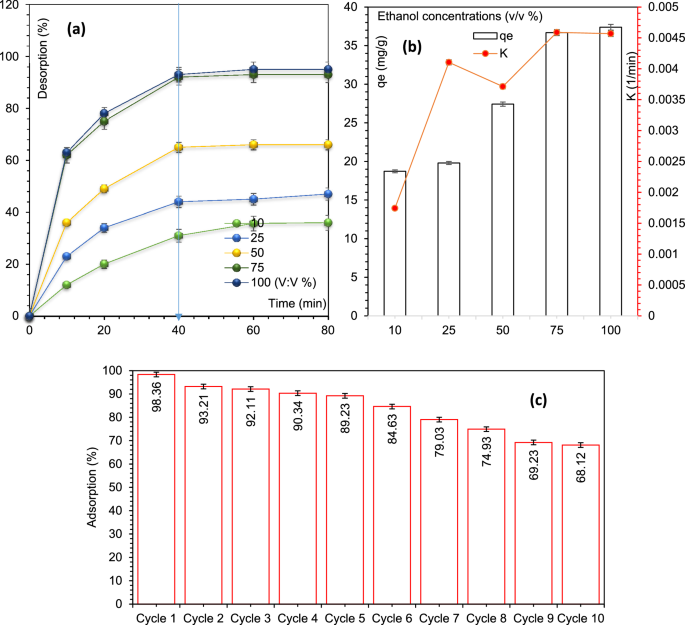
To analyze the desorption and financial feasibility of MIL/Cs@Fe3O4 NCs towards AZT elimination, the adsorbent was recycled with ultrasound + chemical modifications in numerous ethanol concentrations starting from 10 to 100 (v/v p.c). Determine 5a reveals the quantity of desorption towards time at numerous ethanol concentrations beneath optimized circumstances. As proven, the desorption share rose dramatically at numerous ethanol concentrations and reached to equilibrium in 40 min. In Fig. 5a,b, it can be seen that the effectivity (%), capability (mg/g) and charge (ok, based mostly on pseudo-second order kinetic) of desorption course of have an upward development as much as the ethanol concentrations of 75%, however after that no additional enchancment has been noticed. Within the following, the adsorbent’s reusability was evaluated for 10 consecutive cycles. For this function, after every cycle, MIL/Cs@Fe3O4 NCs had been washed with ethanol and distilled water (75% v/v). As noticed from Fig. 5c, the elimination effectivity has decreased by solely 9.13% throughout the first to fifth cycles, and this discount within the adsorption has reached 30.24% within the tenth cycle. The lower in effectivity may be ascribed to the lack of adsorbent mass and the filling of lively websites or practical teams of the adsorbent throughout repeated runs. The quantities of leached aluminium and iron had been 0.024 and 0.147 mg/L within the first cycle, and fell to 0.009 and 0.11 mg/L within the tenth cycle. The leaching of Al and Fe quantities in repeated runs is affordable (Lower than the water normal stage), which proves the soundness and sturdiness of MIL/Cs@Fe3O4 NCs for AZT therapy.
Adsorption mechanism
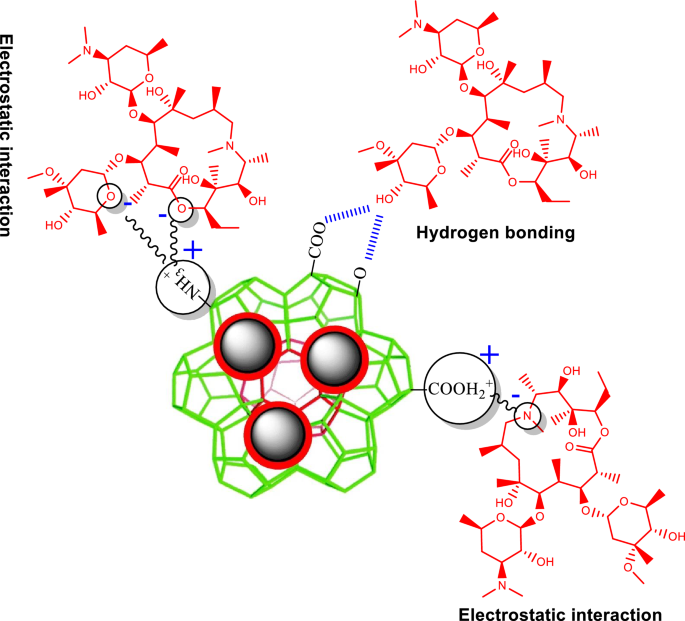
The mechanism of natural compounds’ adsorption is often described by hydrogen bonding, electrostatic interplay, and π–π interplay. MIL/Cs@Fe3O4 NCs used on this research are enriched with π-electrons, amino group (–NH2), and acidic carboxyl group (–COOH) that may play an necessary function within the adsorption mechanism between MIL/Cs@Fe3O4 NCs and AZM by means of hydrogen bonding (H-bonds), electrostatic interplay, and π–π interactions. As may be seen in Fig. S6, AZM is surrounded by excessive quantities of –OH, −CH3, =O, –O–, –N–, –N=, and –OCH3 practical teams. The aforementioned practical teams can play a task in AZM adsorption as follows: (a) –OH concerned to type hydrogen bonding, (b) =O, –O–, –N–, –N=, and –O–CH3 teams contain in anionic electrostatic interactions, and (c) –CH3 group participates in cationic electrostatic interactions. Determine 6 reveals doable adsorption interactions between AZM and MIL/Cs@Fe3O4 NCs. Since there isn’t a π-electron in AZM, it’s unlikely to have π–π interactions with MIL/Cs@Fe3O4 NCs65. Based mostly on the proof, adsorption might happen because of cationic and anionic electrostatic interactions and H-bonding between AZM and MIL/Cs@Fe3O4 NCs.
Research of actual samples
As a way to consider the effectiveness and potential of the MIL/Cs@Fe3O4 NCs for AZT adsorption in actual circumstances, a collection of experiments on faucet water, floor runoff, uncooked wastewater, and secondary effluent had been thought-about beneath optimized circumstances (AZT focus spiked: 10 mg/L). In Supplementary knowledge, Desk S2, the specs of samples are listed. As may be seen, all samples have decrease effectivity in comparison with DI-water. For instance, the effectivity in faucet water was 90.45% whereas the adsorbent efficiency in floor runoff, uncooked and handled wastewater had been 85.34%, 48.45%, and 65%, respectively (Supplementary knowledge, Fig. S7). The lower in AZT adsorption effectivity may be attributed to the presence of TDS, numerous ions, natural compounds, and different contaminants within the precise samples. Based mostly on the outcomes, it may be reported that MIL/Cs@Fe3O4 NCs has an appropriate capability to take away AZT from aqueous samples beneath actual circumstances, though this efficiency has been considerably diminished in uncooked wastewater samples.
Comparability with earlier analysis
The qm parameter of synthesized adsorbent (adsorption functionality based mostly on the Langmuir isotherm mannequin, mg/g) was in contrast with related literature when it comes to adsorbent kind, and the outcomes are summarized in Desk 4. It was noticed that the MIL/Cs@Fe3O4 NCs adsorbent confirmed good capability to compete with related programs for therapy of AZT and has the correct place among the many literature. It needs to be famous that the variations between the adsorption capacities within the numerous adsorbents may be associated to the kind of supplies used (as a result of variability in measurement, floor space, variety of lively websites, and practical teams), adsorbent dosage and the focus of the AZT in experiments. Obtainable proof confirms that the adsorbent synthesized within the current research can have an appropriate and promising efficiency within the elimination of AZT as a consultant of macrolide antibiotics.
[ad_2]
Source_link