Google’s shifting method to AI content material: An in-depth look
[ad_1]
The prevalence of mass-produced, AI-generated content material is making it more durable for Google to detect spam.
AI-generated content material has additionally made judging what’s high quality content material tough for Google.
Nevertheless, indications are that Google is enhancing its skill to determine low-quality AI content material algorithmically.
Spammy AI content material all around the internet
You don’t must be in search engine optimization to know generative AI content material has been discovering its means into Google search outcomes during the last 12 months.
Throughout that point, Google’s angle towards AI-created content material advanced. The official place moved from “it’s spam and breaks our tips” to “our focus is on the standard of content material, fairly than how content material is produced.”
I’m sure Google’s focus-on-quality assertion made it into many inner search engine optimization decks pitching an AI-generated content material technique. Undoubtedly, Google’s stance supplied simply sufficient respiratory room to squeak out administration approval at many organizations.
The consequence: A number of AI-created, low-quality content material flooding the online. And a few of it initially made it into the corporate’s search outcomes.
Invisible junk
The “seen internet” is the sliver of the online that engines like google select to index and present in search outcomes.
We all know from How Google Search and rating works, in response to Google’s Pandu Nayak, based mostly on Google antitrust trial testimony, that Google “solely” maintains an index of ~400 billion paperwork. Google finds trillions of paperwork throughout crawling.
Meaning Google indexes solely 4% of the paperwork it encounters when crawling the online (400 billion/10 trillion).
Google claims to guard searchers from spam in 99% of question clicks. If that’s even remotely correct, it’s already eliminating many of the content material not value seeing.
Content material is king – and the algorithm is the Emperor’s new garments
Google claims it’s good at figuring out the standard of content material. However many SEOs and skilled web site managers disagree. Most have examples demonstrating inferior content material outranking superior content material.
Any respected firm investing in content material is more likely to rank within the prime few % of “good” content material on the net. Its rivals are more likely to be there, too. Google has already eradicated a ton of lesser candidates for inclusion.
From Google’s perspective, it’s carried out a implausible job. 96% of paperwork didn’t make the index. Some points are apparent to people however tough for a machine to identify.
I’ve seen examples that result in the conclusion Google is proficient at understanding which pages are “good” and are “unhealthy” from a technical perspective, however comparatively ineffective at decerning good content material from nice content material.
Google admitted as a lot in DOJ anti-trust reveals. In a 2016 presentation says: “We don’t perceive paperwork. We faux it.”

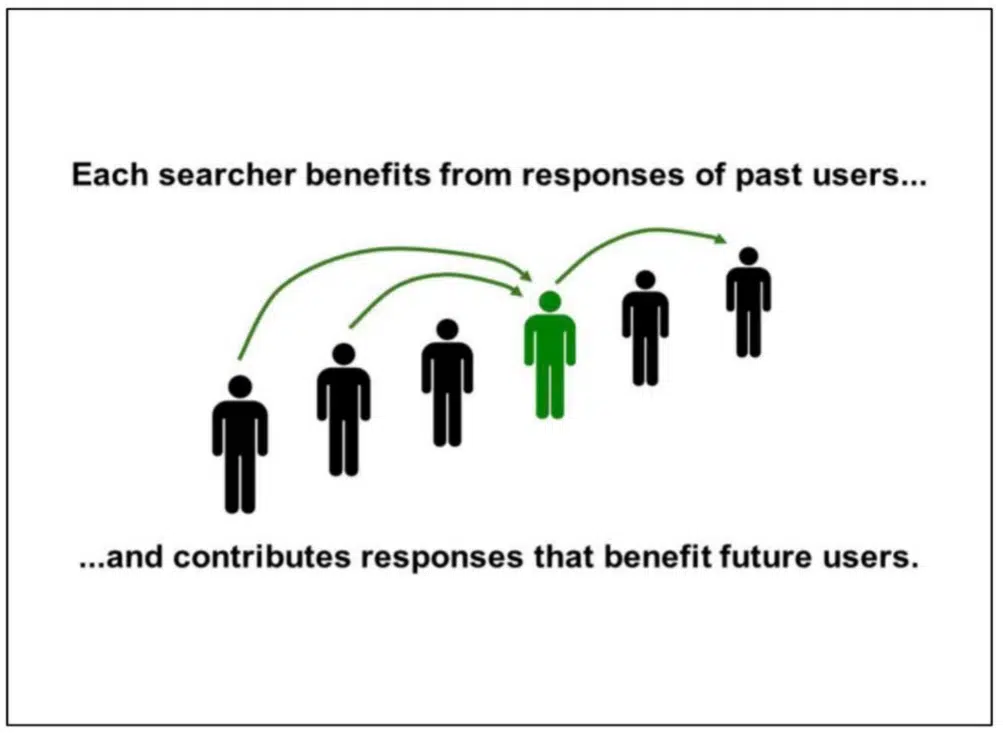
Google depends on consumer interactions on SERPs to evaluate content material high quality
Google has relied on consumer interactions with SERPs to know how “good” the contents of a doc is. Google explains later the presentation: “Every searcher advantages from the responses of previous customers… and contributes responses that profit future customers.”
The interplay information Google makes use of to evaluate high quality has at all times been a hotly debated subject. I consider Google makes use of interactions nearly solely from their SERPs, not from web sites, to make choices about content material high quality. Doing so guidelines out site-measured metrics like bounce price.
For those who’ve been listening carefully to the individuals who know, Google has been pretty clear that it makes use of click on information to rank content material.
Google engineer Paul Haahr offered “How Google Works: A Google Rating Engineer’s Story,” at SMX West in 2016. Haahr spoke about Google’s SERPs and the way the search engine “seems to be for modifications in click on patterns.” He added that this consumer information is “more durable to know than you would possibly anticipate.”
Haahr’s remark is additional strengthened within the “Rating for Analysis” presentation slide, which is a part of the DOJ reveals:

Google’s skill to interpret consumer information and switch it into one thing actionable depends on understanding the cause-and-effect relationship between altering variables and their related outcomes.
The SERPs are the one place Google can use to know which variables are current. Interactions on web sites introduce an enormous variety of variables past Google’s view.
Even when Google may determine and quantify interactions with web sites (which might arguably be harder than assessing the standard of content material), there could be a knock-on impact with the exponential progress of various units of variables, every requiring minimal visitors thresholds to be met earlier than significant conclusions might be made.
Google acknowledges in its paperwork that “rising UX complexity makes suggestions progressively laborious to transform into correct worth judgments” when referring to the SERPs.
Get the every day e-newsletter search entrepreneurs depend on.
Manufacturers and the cesspool
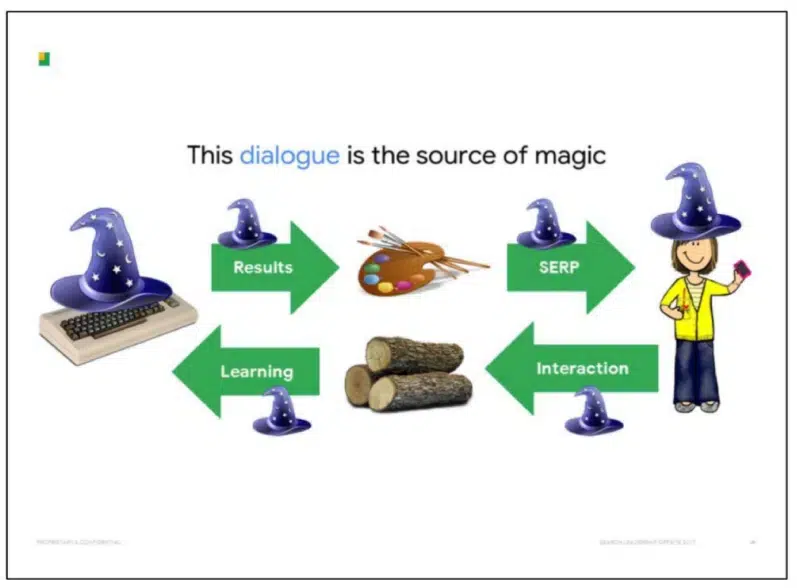
Google says the “dialogue” between SERPs and customers is the “supply of magic” in the way it manages to “faux” the understanding of paperwork.
Outdoors of what we’ve seen within the DOJ reveals, clues to how Google makes use of consumer interplay in rankings are included in its patents.
One that’s notably attention-grabbing to me is the “Website high quality rating,” which (to grossly oversimplify) seems to be at relationships resembling:
- When searchers embody model/navigational phrases of their question or when web sites embody them of their anchors. For example, a search question or hyperlink anchor for “search engine marketing information searchengineland” fairly than “search engine marketing information.”
- When customers seem like deciding on a particular consequence inside the SERP.
These alerts might point out a website is an exceptionally related response to the question. This technique of judging high quality aligns with Google’s Eric Schmidt saying, “manufacturers are the answer.”
This is sensible in mild of research that present customers have a powerful bias towards manufacturers.
For example, when requested to carry out a analysis job resembling looking for a celebration gown or trying to find a cruise vacation, 82% of contributors chosen a model they have been already aware of, no matter the place it ranked on the SERP, in response to a Crimson C survey.
Manufacturers and the recall they trigger are costly to create. It is sensible that Google would depend on them in rating search outcomes.
What does Google contemplate AI spam?
Google revealed steerage on AI-created content material this 12 months, which refers to its Spam Insurance policies the outline outline content material that’s “meant to govern search outcomes.”
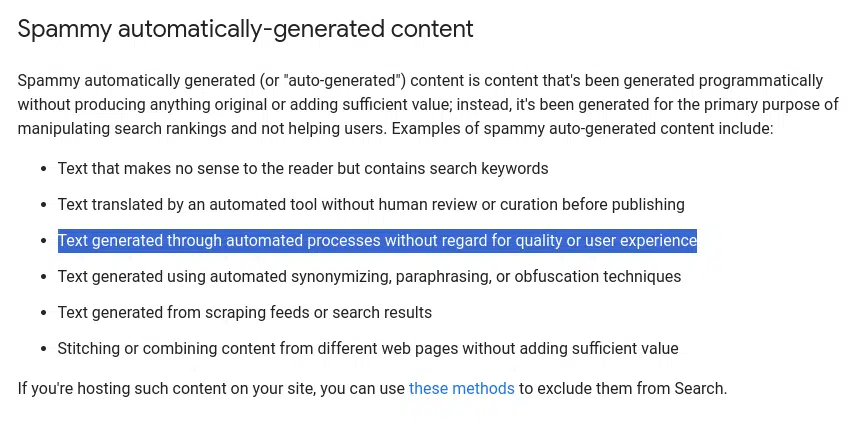
Spam is “Textual content generated by means of automated processes with out regard for high quality or consumer expertise,” in response to Google’s definition. I interpret this as anybody utilizing AI programs to provide content material with out a human QA course of.
Arguably, there might be instances the place a generative-AI system is skilled on proprietary or personal information. It might be configured to have extra deterministic output to cut back hallucinations and errors. You could possibly argue that is QA earlier than the very fact. It’s more likely to be a rarely-used tactic.
All the pieces else I’ll name “spam.”
Producing this sort of spam was once reserved for these with the technical skill to scrape information, construct databases for madLibbing or use PHP to generate textual content with Markov chains.
ChatGPT has made spam accessible to the plenty with a couple of prompts and a straightforward API and OpenAI’s ill-enforced Publication Coverage, which states:
“The function of AI in formulating the content material is clearly disclosed in a means that no reader may probably miss, and {that a} typical reader would discover sufficiently simple to know.”

The amount of AI-generated content material being revealed on the net is gigantic. A Google Seek for “regenerate response -chatgpt -results” shows tens of 1000’s of pages with AI content material generated “manually” (i.e., with out utilizing an API).
In lots of instances QA has been so poor “authors” left within the “regenerate response” from the older variations of ChatGPT throughout their copy and paste.
Patterns of AI content material spam
When GPT-3 hit, I needed to see how Google would react to unedited AI-generated content material, so I arrange my first check web site.
That is what I did:
- Purchased a model new area and arrange a primary WordPress set up.
- Scraped the highest 10,000 video games that have been promoting on Steam.
- Fed these video games into the AlsoAsked API to get the questions being requested by them.
- Used GPT-3 to generate solutions to those questions.
- Generate FAQPage schema for every query and reply.
- Scraped the URL for a YouTube video in regards to the recreation to embed on the web page.
- Use the WordPress API to create a web page for every recreation.
There have been no advertisements or different monetization options on the positioning.
The entire course of took a couple of hours, and I had a brand new 10,000-page web site with some Q&A content material about widespread video video games.
Each Bing and Google ate up the content material and, over a interval of three months, listed most pages. At its peak, Google delivered over 100 clicks per day, and Bing much more.

Outcomes of the check:
- After about 4 months, Google determined to not rank some content material, leading to a 25% hit in visitors.
- A month later, Google stopped sending visitors.
- Bing stored sending visitors for your entire interval.
Probably the most attention-grabbing factor? Google didn’t seem to have taken handbook motion. There was no message in Google Search Console, and the two-step discount in visitors made me skeptical that there had been any handbook intervention.
I’ve seen this sample repeatedly with pure AI content material:
- Google indexes the positioning.
- Visitors is delivered rapidly with regular positive factors week on week.
- Visitors then peaks, which is adopted by a speedy decline.
One other instance is the case of Informal.ai. On this “search engine optimization heist,” a competitor’s sitemap was scraped and 1,800+ articles have been generated with AI. Visitors adopted the identical sample, climbing a number of months earlier than stalling, then a dip of round 25% adopted by a crash that eradicated almost all visitors.
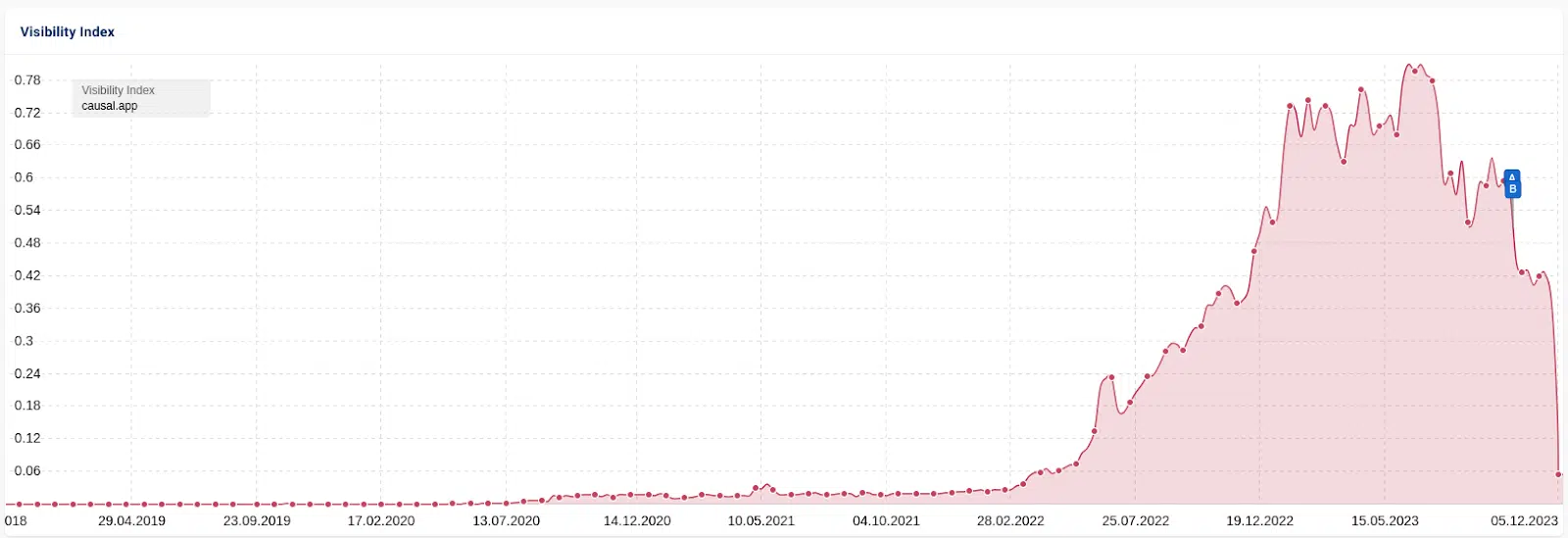
There may be some dialogue within the search engine optimization group about whether or not this drop was a handbook intervention due to all of the press protection it acquired. I consider the algorithm was at work.
An identical and maybe extra attention-grabbing case research concerned LinkedIn’s “collaborative” AI articles. These AI-generated articles created by LinkedIn invited customers to “collaborate” with fact-checking, corrections and additions. It rewarded “prime contributors” with a LinkedIn badge for his or her efforts.
As with the opposite instances, visitors rose after which dropped. Nevertheless, LinkedIn maintained some visitors.
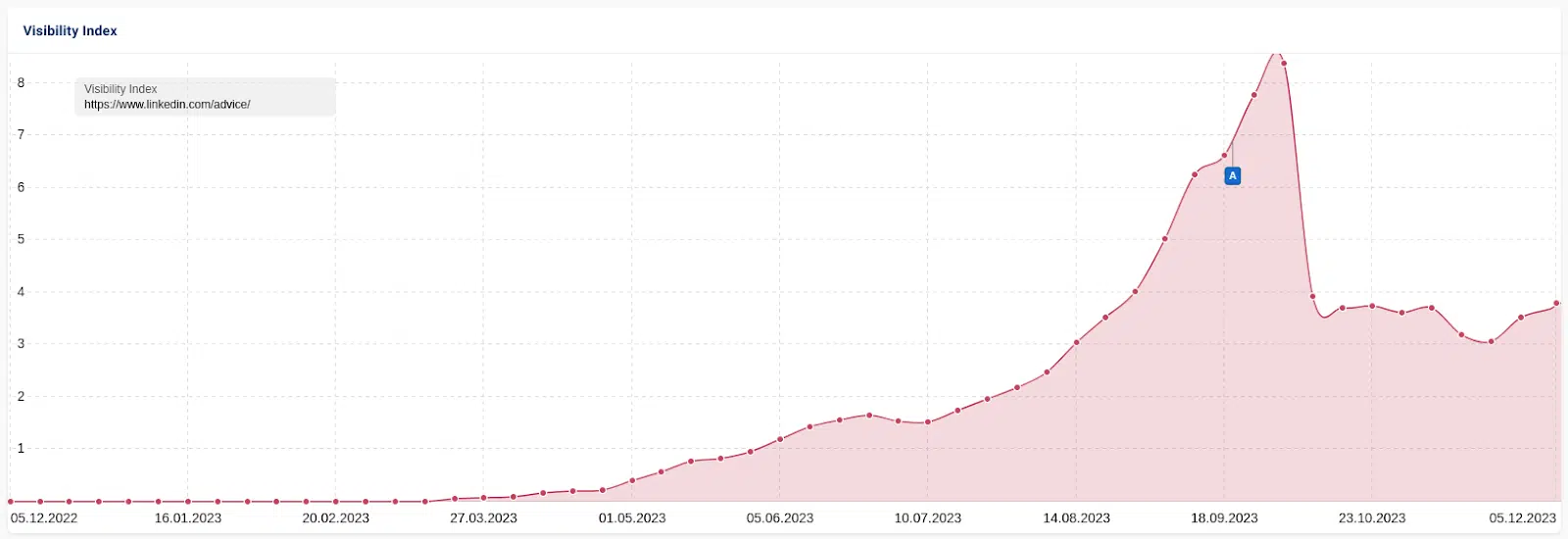
This information signifies that visitors fluctuations consequence from an algorithm fairly than a handbook motion.
As soon as edited by a human, some LinkedIn collaborative articles apparently met the definition of helpful content material. Others weren’t, in Google’s estimation.
Perhaps Google’s acquired it proper on this occasion.
If it’s spam, why does it rank in any respect?
From every thing I’ve seen, rating is a multi-stage course of for Google. Time, expense, and limits on information entry forestall the implementation of extra complicated programs.
Whereas the evaluation of paperwork by no means stops, I consider there’s a lag earlier than Google’s programs detect low-quality content material. That’s why you see the sample repeat: content material passes an preliminary “sniff check,” solely to be recognized later.
Let’s check out a number of the proof for this declare. Earlier on this article, we skimmed over Google’s “Website High quality” patent and the way they leverage consumer interplay information to generate this rating for rating.
When a website is model new, customers haven’t interacted with the content material on the SERP. Google can’t entry the standard of the content material.
Properly, one other patent for Predicting Website High quality covers this example.
Once more, to grossly oversimplify, a top quality rating for brand new websites is predicted by first acquiring a relative frequency measure for every of a wide range of phrases discovered on the brand new website.
These measures are then mapped utilizing a beforehand generated phrase mannequin constructed from high quality scores established from beforehand scored websites.
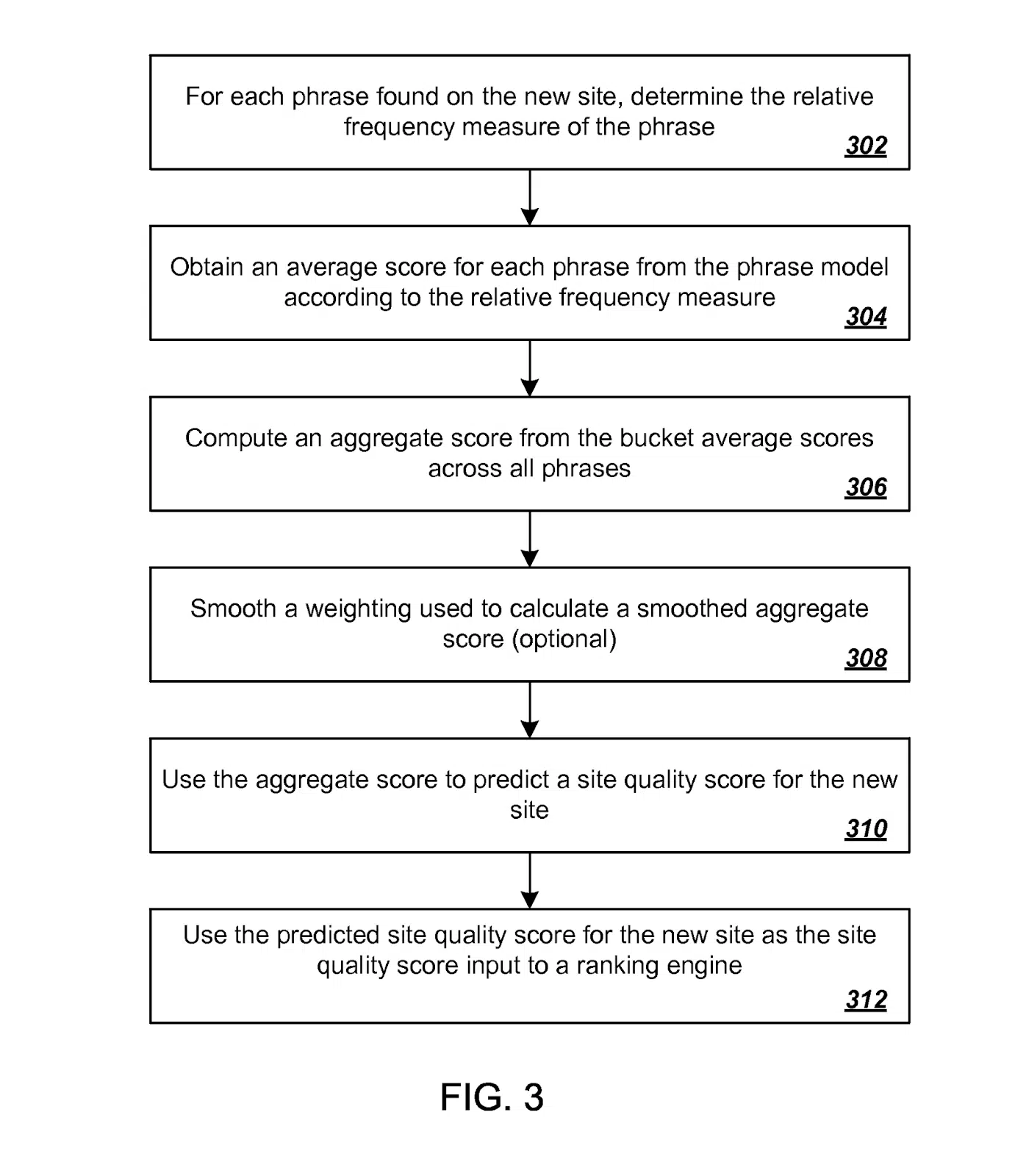
If Google have been nonetheless utilizing this (which I consider they’re, a minimum of a small means), it might imply that many new web sites are ranked on a “first guess” foundation with a top quality metric included within the algorithm. Later, the rating is refined based mostly on consumer interplay information.
I’ve noticed, and lots of colleagues agree, that Google typically elevates websites in rating for what seems to be a “check interval.”
Our concept on the time was there was a measurement occurring to see if consumer interplay matched Google’s predictions. If not, visitors fell as rapidly because it rose. If it carried out properly, it continued to get pleasure from a wholesome place on the SERP.
A lot of Google’s patents have references to “implicit consumer suggestions,” together with this very candid assertion:
“A rating sub-system can embody a rank modifier engine that makes use of implicit consumer suggestions to trigger re-ranking of search outcomes as a way to enhance the ultimate rating offered to a consumer.”
AJ Kohn wrote about this sort of information intimately again in 2015.
It’s value noting that that is an previous patent and considered one of many. Since this patent was revealed, Google has developed many new options, resembling:
- RankBrain, which has particularly been cited to deal with “new” queries for Google.
- SpamBrain, considered one of Google’s foremost instruments for combatting webspam.
Google: Thoughts the hole
I don’t suppose anybody exterior of these with first-hand engineering data at Google is aware of precisely how a lot consumer/SERP interplay information could be utilized to particular person websites fairly than the general SERP.
Nonetheless, we all know that trendy programs resembling RankBrain are a minimum of partly skilled on consumer click on information.
One factor additionally piqued my curiosity in AJ Kohn’s evaluation of the DOJ testimony on these new programs. He writes:
“There are a selection of references to transferring a set of paperwork from the ‘inexperienced ring to the ‘blue ring.’ These all confer with a doc that I’ve not but been in a position to find. Nevertheless, based mostly on the testimony it appears to visualise the way in which Google culls outcomes from a big set to a smaller set the place they’ll then apply additional rating elements.”
This helps my sniff-test concept. If an internet site passes, it will get moved to a distinct “ring” for extra computationally or time-intensive processing to enhance accuracy.
I consider this to be the present scenario:
- Google’s present rating programs can’t maintain tempo with AI-generated content material creation and publication.
- As gen-AI programs produce grammatically appropriate and principally “wise” content material, they move Google’s “sniff exams” and can rank till additional evaluation is full.
Herein lies the issue: the pace at which this content material is being created with generative AI means there’s an never-ending queue of websites ready for Google’s preliminary analysis.
An HCU hop to UGC to beat the GPT?
I consider Google is aware of that is one main problem they face. If I can take pleasure in some wild hypothesis, it’s attainable that latest Google updates, such because the useful content material replace (HCU), have been utilized to compensate for this weak point.
It’s no secret the HCU and “hidden gems” programs benefited user-generated content material (UGC) websites resembling Reddit.
Reddit was already some of the visited web sites. Current Google modifications yielded greater than double its search visibility, on the expense of different web sites.
My conspiracy concept is that UGC websites, with a couple of notable exceptions, are a number of the least probably locations to search out mass-produced AI, as a lot content material is moderated.
Whereas they will not be “excellent” search outcomes, the general satisfaction of trawling by means of some uncooked UGC could also be greater than Google constantly rating no matter ChatGPT final vomited onto the online.
The deal with UGC could also be a short lived repair to spice up high quality; Google can’t deal with AI spam quick sufficient.
What does Google’s long-term plan appear like for AI spam?
A lot of the testimony about Google within the DOJ trial got here from Eric Lehman, a former 17-year worker who labored there as a software program engineer on search high quality and rating.
One recurring theme was Lehman’s claims that Google’s machine studying programs, BERT and MUM, have gotten extra essential than consumer information. They’re so highly effective that it’s probably Google will rely extra on them than consumer information sooner or later.
With slices of consumer interplay information, engines like google have a superb proxy for which they’ll make choices. The limitation is gathering sufficient information quick sufficient to maintain up with modifications, which is why some programs make use of different strategies.
Suppose Google can construct their fashions utilizing breakthroughs resembling BERT to massively enhance the accuracy of their first content material parsing. In that case, they can shut the hole and drastically cut back the time it takes to determine and de-rank spam.
This downside exists and is exploitable. The stress on Google to handle its shortcomings will increase as extra individuals seek for low-effort, high-results alternatives.
Satirically, when a system turns into efficient in combatting a particular kind of spam at scale, the system could make itself nearly redundant as the chance and motivation to participate is diminished.
Fingers crossed.
Opinions expressed on this article are these of the visitor creator and never essentially Search Engine Land. Employees authors are listed right here.
[ad_2]
Source_link






