Optimization of the method of seed extraction from the Larix decidua Mill. cones together with analysis of seed amount and high quality
[ad_1]
Cone traits: all the set and particular person variants
Cones utilized in all of the take a look at variants didn’t differ from one another by way of top (coefficient of variance within the Scholar t-test–F = 1.33 at p = 0.23), diameter (F = 1.77 at p = 0.08), or preliminary weight (F = 0.86 at p = 0.55). Evaluation of variance revealed a major distinction for cone humidity (F = 2.52 at p ˂ 0.05).
Cone parameters resembling top, diameter and preliminary weight are elements that may decide the course of the extraction course of. Due to this fact, the connection between diameter and top for all cones used within the research was described utilizing a linear regression equation ((y=0.2794x+8.3195)), which signifies that cone diameter elevated by 0.28 mm per 1 mm of cone top, ((R=0.778>0.104-{R}_{kr})).
The preliminary weight of cones could also be related to their harvest time or storage situations. A linear regression equation was additionally used to explain the connection between the peak and preliminary weight of the examined cones (y = 0.238x–3.918), which signifies that preliminary weight elevated on common by 0.238 g per 1 mm of top, (R = 0.795 > 0.104).
Desk 2 exhibits means with customary deviations, the minimal and most values of the measured parameters, the vary of variance, the coefficient of variation and the usual error for all the set of studied cones and seeds. The Shapiro–Wilk take a look at confirmed that the examined traits had a traditional distribution.
The cones used within the research had a top of 21.4–44.1 mm and a diameter of 12.5–24.3 mm. The imply top of a cone was 33.8 (± 3.4) mm and the imply diameter was 17.8 (± 1.6) mm. The preliminary weight of cones ranged from 2.137 to 9.111 g, with a imply of 4.144 (± 1.019) g. The preliminary moisture content material of cones was from 27.6 to 57.1%, with a imply of 40.4 (± 4.5)%. Evaluation was carried out for particular person extraction variants. The imply values of cone top h, diameter d, preliminary weight m01, and moisture content material W had been calculated (Desk 3).
The HSD Tukey take a look at revealed one homogeneous group for cone top encompassing all variants and two homogeneous teams for diameter. The primary group consisted of all variants besides 7, and the second group included all variants besides 2. One homogeneous group was obtained for preliminary weight. Two homogeneous teams had been discovered for moisture content material, one consisting of all variants besides 7, and the opposite one containing variants 1, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, and 9.
Seed extraction outcomes for the studied steps
Seed extraction situations and time
The change in cone weight in every step of the extraction course of trusted its period, temperature and humidity situations within the extraction cupboard, in addition to on the preliminary moisture content material of the cones.
Humidity contained in the drying chamber decreased to a mean of 30% after 2 h of the method in every step because of rising temperature. Over the following 4 h of the method, after rising the temperature, the humidity contained in the chamber declined considerably, after which (over 2 and 4 h) it decreased additional solely barely, stabilizing at approx. 5% for the ten h variants, 6% for the 8 h variants, and eight% for six h variants on common.
Moisture content material modifications in cones through the seed extraction course of
The preliminary moisture content material (u01) of the studied cones was a lot higher than 0.20 ({mathrm{kg}}_{mathrm{water}}cdot {mathrm{kg}}_{mathrm{d}.mathrm{w}.}^{-1}), which signifies that particular care have to be taken throughout seed extraction, which ought to be performed at a temperature of as much as 50 °C8.
The comparatively excessive moisture content material of the cones could possibly be attributed to the absence of preliminary drying in ethereal storage locations previous to seed extraction (which is often the case in business follow) and the early date of cone harvest, at the start of the extraction season. The preliminary (u0x) and ultimate (ukx) moisture content material of cones utilized in every course of variant is given with customary deviation in Desk 4.
The preliminary moisture content material of cones (u0x) in most variants elevated with every extraction step as a consequence of immersion. In most variants, the ultimate moisture content material (ukx) was the very best within the first extraction step and decreased or remained on the identical stage with every subsequent step.
The imply preliminary moisture content material for the three course of variants with 10 h of drying was 0.411 ({mathrm{kg}}_{mathrm{water}}cdot {mathrm{kg}}_{mathrm{d}.mathrm{w}.}^{-1}). After 10 h of drying, the imply moisture content material decreased to 0.130 ({mathrm{kg}}_{mathrm{water}}cdot {mathrm{kg}}_{mathrm{d}.mathrm{w}.}^{-1}). The imply preliminary moisture content material within the fifth extraction step was 0.437 ({mathrm{kg}}_{mathrm{water}}cdot {mathrm{kg}}_{mathrm{d}.mathrm{w}.}^{-1}), and the ultimate moisture content material in that step was 0.071 ({mathrm{kg}}_{mathrm{water}}cdot {mathrm{kg}}_{mathrm{d}.mathrm{w}.}^{-1}) . Cones dried for 10 h reached on common 7% moisture content material after extraction steps 4 and 5.
The imply preliminary moisture content material for the three course of variants with 8 h of drying was 0.412 ({mathrm{kg}}_{mathrm{water}}cdot {mathrm{kg}}_{mathrm{d}.mathrm{w}.}^{-1}). After 8 h of drying, the imply moisture content material decreased to 0.128 ({mathrm{kg}}_{mathrm{water}}cdot {mathrm{kg}}_{mathrm{d}.mathrm{w}.}^{-1}) . The imply preliminary moisture content material within the fifth extraction step was 0.440 ({mathrm{kg}}_{mathrm{water}}cdot {mathrm{kg}}_{mathrm{d}.mathrm{w}.}^{-1}), and the ultimate moisture content material in that step was 0.064 ({mathrm{kg}}_{mathrm{water}}cdot {mathrm{kg}}_{mathrm{d}.mathrm{w}.}^{-1}) . Cones dried for 8 h reached on common 7.1% moisture content material after extraction step IV and 6.4% after step V.
The imply preliminary moisture content material for the three course of variants with 6 h of drying was 0.389 ({mathrm{kg}}_{mathrm{water}}cdot {mathrm{kg}}_{mathrm{d}.mathrm{w}.}^{-1}). After 6 h of drying, the imply moisture content material decreased to 0.129 ({mathrm{kg}}_{mathrm{water}}cdot {mathrm{kg}}_{mathrm{d}.mathrm{w}.}^{-1}) . The imply preliminary moisture content material within the fifth extraction step was 0.415 ({mathrm{kg}}_{mathrm{water}}cdot {mathrm{kg}}_{mathrm{d}.mathrm{w}.}^{-1}), and the ultimate moisture content material in that step was 0.084 ({mathrm{kg}}_{mathrm{water}}cdot {mathrm{kg}}_{mathrm{d}.mathrm{w}.}^{-1}) . Cones dried for six h reached on common 8.9% moisture content material after extraction step IV and eight.4% moisture content material after step V, which signifies that their ultimate moisture content material was greater than that of cones dried for 8 h and 10 h.
The cones with the longest immersion time (15 min) had been characterised by the very best preliminary moisture content material in every extraction step as in comparison with the opposite two variants (immersion of 5 min and 10 min) with the identical drying time. The ultimate moisture content material in a given extraction step differed between cones with totally different immersion instances. Cones with an immersion time of 15 min had been characterised by the very best ultimate moisture content material in particular person extraction steps, and people with 5 min immersion revealed the bottom ultimate moisture content material.
The Tukey HSD take a look at revealed homogeneous teams by way of preliminary moisture content material (u01, u02, u03, u04, u05) and ultimate moisture content material (uk1, uk2, uk3, uk4, uk5) in every step, as proven in Desk 4. As an illustration, 4 homogeneous teams had been discovered for the ultimate moisture content material after extraction step V (uk5): the primary one consisted of all variants aside from 7, 8, and 9, the second included variants 1, 2, 3, and seven, the third one comprised of variants 7 and eight, whereas the fourth one was constituted by variant 9 alone.
Utilizing Eq. (1), modifications in moisture content material had been described for every of the examined cones over all 5 steps of every variant. The equation included the preliminary and ultimate values of moisture content material and the b coefficient for particular person cones. The common values of the b coefficient and customary deviations for every extraction step are introduced in Desk 5 for particular person extraction variants.
The bottom worth of the b coefficient was recorded for step one of the 10h_15min variant (b1 = 0.34), whereas the very best worth was obtained for the fifth step of the 8 h_15 min variant (b5 = 0.60). Within the course of variants involving 10 and eight h of drying , the b coefficient elevated with every extraction step till the third one; within the fourth step it barely decreased and within the fifth step it remained fixed. Within the variants with 6 h of drying the b coefficient nearly peaked within the second extraction step and remained at an analogous stage till the fifth step. Within the first steps of the variants with 6 h of drying, the imply worth of the b coefficient was 0.54 and didn’t differ considerably from the coefficients obtained through the different steps. It was famous that within the 8 h_15 min variant, the b coefficients elevated over successive steps.
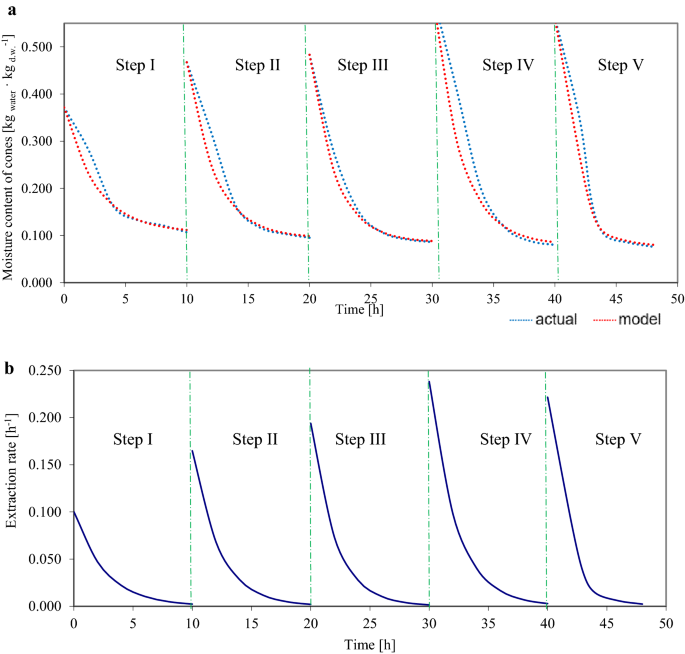
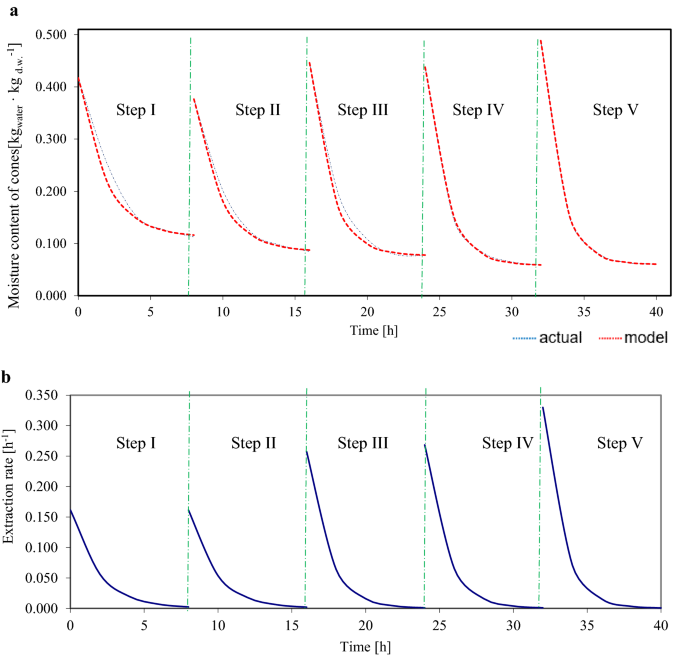
Figures 2–3 present examples of curves of precise and mannequin modifications in moisture content material and the speed of extraction for pattern cones, one every for variants 10 h_15 min and eight h_15 min.
Equations for modifications in moisture content material and extraction fee in consecutive extraction steps are given beneath for the graphically for the cone proven in Fig. 2 (no. 32 within the 10 h_15 min variant):
Step I: ({u}_{1}=0.264cdot {mathrm{e }}^{left(-0.38 cdot {tau }_{i}proper)}+0.107) ,(frac{d{u}_{1}}{d{tau }_{1}}=-0.100cdot {mathrm{e }}^{(-0.38 cdot {tau }_{i})})
Step II: ({u}_{2}=0.372cdot {mathrm{e }}^{left(-0.44 cdot {tau }_{i}proper)}+0.095) , (frac{d{u}_{1}}{d{tau }_{1}}=-0.164cdot {mathrm{e }}^{(-0.44 cdot {tau }_{i})})
Step III: ({u}_{3}=0.397cdot {mathrm{e }}^{left(-0.49 cdot {tau }_{i}proper)}+0.086) , (frac{d{u}_{1}}{d{tau }_{1}}=-0.195cdot {mathrm{e }}^{(-0.49 cdot {tau }_{i})})
Step IV: ({u}_{4}=0.536cdot {mathrm{e }}^{left(-0.44 cdot {tau }_{i}proper)}+0.080) , (frac{d{u}_{1}}{d{tau }_{1}}=-0.236cdot {mathrm{e }}^{(-0.44 cdot {tau }_{i})})
Step V: ({u}_{5}=0.485cdot {mathrm{e }}^{left(-0.46 cdot {tau }_{i}proper)}+0.076) , (frac{d{u}_{1}}{d{tau }_{1}}=-0.223cdot {mathrm{e }}^{(-0.46 cdot {tau }_{i})})
Equations for modifications (Fig. 3) in moisture content material and extraction fee in consecutive extraction steps are additionally given for this cone (no. 17 within the 8 h_15 min variant):
Step I: ({u}_{1}=0.304cdot {mathrm{e }}^{left(-0.53 cdot {tau }_{i}proper)}+0.113) ,(frac{d{u}_{1}}{d{tau }_{1}}=-0.161cdot {mathrm{e }}^{(-0.53 cdot {tau }_{i})})
Step II: ({u}_{2}=0.292cdot {mathrm{e }}^{left(-0.55 cdot {tau }_{i}proper)}+0.085) , (frac{d{u}_{1}}{d{tau }_{1}}=-0.161cdot {mathrm{e }}^{(-0.55 cdot {tau }_{i})})
Step III: ({u}_{3}=0.369cdot {mathrm{e }}^{left(-0.70 cdot {tau }_{i}proper)}+0.077) , (frac{d{u}_{1}}{d{tau }_{1}}=-0.258cdot {mathrm{e }}^{(-0.70 cdot {tau }_{i})})
Step IV: ({u}_{4}=0.379cdot {mathrm{e }}^{left(-0.71 cdot {tau }_{i}proper)}+0.059) , (frac{d{u}_{1}}{d{tau }_{1}}=-0.269cdot {mathrm{e }}^{(-0.71 cdot {tau }_{i})})
Step V: ({u}_{5}=0.428cdot {mathrm{e }}^{left(-0.77 cdot {tau }_{i}proper)}+0.060) , (frac{d{u}_{1}}{d{tau }_{1}}=-0.330cdot {mathrm{e }}^{(-0.77 cdot {tau }_{i})})
Lastly, equations for modifications in moisture content material and extraction fee in consecutive extraction steps are given for cone no. 5 within the 6 h_15 min variant:
Step I: ({u}_{1}=0.308cdot {mathrm{e }}^{left(-0.58 cdot {tau }_{i}proper)}+0.0904) ,(frac{d{u}_{1}}{d{tau }_{1}}=-0.179cdot {mathrm{e }}^{(-0.58 cdot {tau }_{i})})
Step II: ({u}_{2}=0.346cdot {mathrm{e }}^{left(-0.63 cdot {tau }_{i}proper)}+0.1070) , (frac{d{u}_{1}}{d{tau }_{1}}=-0.218cdot {mathrm{e }}^{(-0.63 cdot {tau }_{i})})
Step III: ({u}_{3}=0.368cdot {mathrm{e }}^{left(-0.63 cdot {tau }_{i}proper)}+0.0837) , (frac{d{u}_{1}}{d{tau }_{1}}=-0.232cdot {mathrm{e }}^{(-0.63 cdot {tau }_{i})})
Step IV: ({u}_{4}=0.387cdot {mathrm{e }}^{left(-0.68 cdot {tau }_{i}proper)}+0.0838) , (frac{d{u}_{1}}{d{tau }_{1}}=-0.263cdot {mathrm{e }}^{(-0.68 cdot {tau }_{i})})
Step V: ({u}_{5}=0.396cdot {mathrm{e }}^{left(-0.65 cdot {tau }_{i}proper)}+0.0743) , (frac{d{u}_{1}}{d{tau }_{1}}=-0.257cdot {mathrm{e }}^{(-0.65 cdot {tau }_{i})})
Figures 2a, 3a present the curves of precise modifications within the moisture content material of three pattern cones subjected to totally different drying instances (10 and eight h) however the identical immersion time (15 min); the curves had been fitted to a mannequin which is extensively utilized in descriptions of drying at fixed temperature (principally for greens). The current research used variable temperature, which can have influenced the match of the mannequin, along with the enter variables (drying and immersion instances). The perfect match was discovered for the cone subjected to the variant with 8 h of drying (Fig. 3), with a slight deviation within the first three extraction steps, and with an excellent match within the fourth and fifth steps. The bottom match was discovered for the cone subjected to six h drying, which can be attributable to inadequate drying time (the cone was uncovered to 35 °C for two h, and to 50 °C for under 4 h).
Figures 2b, 3b present diagrams for cone extraction charges at totally different drying instances (10 h and eight h) on the identical immersion instances (15 min). As could be seen, extraction charges decreased within the very starting, which is attribute of the so-called second interval of strong drying (Pabis44).
Seed extraction dynamics
Desk 2 presents knowledge on the variety of scales and seeds for the studied cones. There have been from 33 to 70 open scales per cone, with a mean of 48 (± 6). From 1 to 76 seeds had been extracted per cone, with a mean of 36 (± 18). Lastly, every cone contained from 5 to 97 seeds, with a mean of 52 (± 19). The load of the extracted seeds ranged from 0.001 g to 0.651 g, on common 0.193 (± 0.109) g.
Cones obtained from totally different course of variants didn’t differ by way of the variety of seeds extracted (F = 0.862 at p = 0.55) or their weight (F = 0.720 at p = 0.674). Nonetheless, ANOVA did reveal important variations within the variety of scales (F = 3.561 at p ˂0.05) and the overall variety of seeds per cone (F = 2.93601 at p = 0.003645). Desk 6 provides imply scale and seed numbers per larch cone (with customary deviations) for the varied extraction variants and homogeneous teams.
On common, 70% of the seeds had been extracted from cones utilized in all 9 research variants, with 30% of the seeds remaining within the cones. Desk 7 exhibits the variety of seeds extracted in particular person variants and the variety of seeds remaining within the cones, expressed as a share.
The best variety of seeds was obtained in course of variants 2–73%, carefully adopted by variants 3, 1, and seven (72%), and eight (70%). The bottom seed yield was obtained from variant 4 (65%).
In all research variants, a number of the seeds had been obtained within the technique of extraction within the chamber and a few within the technique of shaking within the drum (Desk 7). The very best variety of seeds within the chamber was obtained in variant 2 (69%), and the bottom in variant 9 (56%). On common, the biggest amount of seeds was obtained within the chamber within the 10 h variants, and the bottom amount within the 6 h variants. Evaluating totally different course of variants of the identical drying period, the best variety of seeds within the chamber had been obtained in variants 2, 5, and seven (and likewise in variant 8—just one% fewer). The best amount of seeds extracted by shaking within the drum was obtained in variant 9 (44%), and the bottom in variant 2 (31%). On common, 38% of seeds extracted in all variants had been obtained by shaking within the drum.
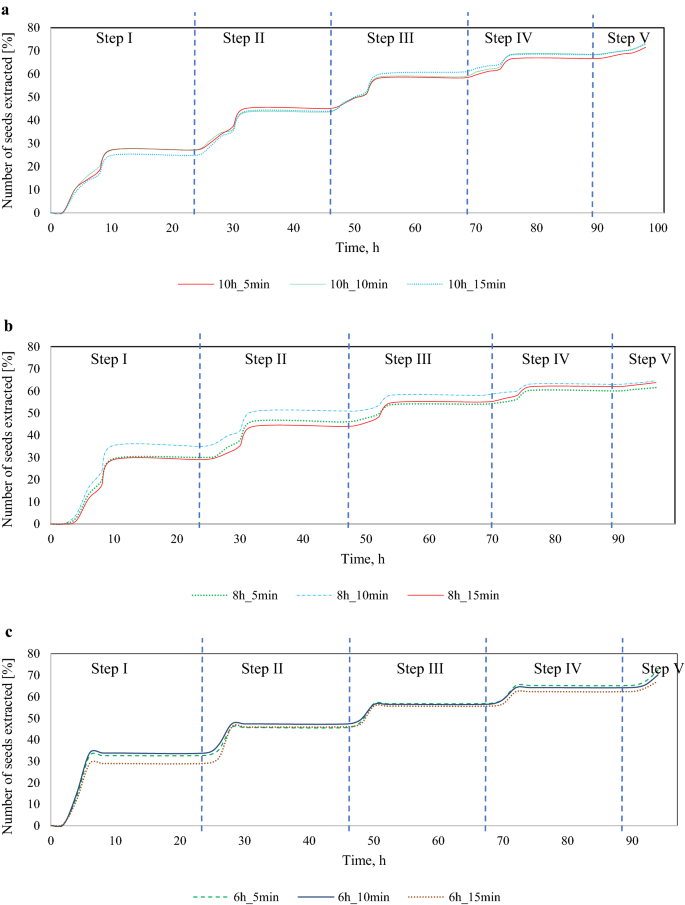
It may be seen that in every of the variants and their particular person steps, the very best variety of seeds was obtained after 6 h of the method. Determine 4a–c exhibits the share of seeds obtained through the efficient extraction time, the place the variety of seeds extracted at a given step was added cumulatively to these from the earlier steps.
The diagrams in Fig. 4 present the share of seeds obtained all through all the course of. Every step consists of drying, shaking, immersion, and soaking, aside from step V, which concerned solely drying and shaking with out immersion or soaking. Evaluation of seed yield over 10 h of drying (Fig. 4a) exhibits that on common 37% of all extracted seeds had been obtained in step one, 26% within the second step, approx. 20% within the third step, 11% within the fourth step, and about 6% within the fifth step.
As regards the 8 h course of (Fig. 4b), on common 30% of all extracted seeds had been obtained within the within the first extraction step within the 8 h_5 min and eight h_15 min variants, and as a lot as 53% within the 8 h_10 min variant. A median of 27% of all seeds had been extracted within the second step, 15% within the third step, about 11% within the fourth step, and approx. 5% within the fifth step. The 8 h_10 min variant was characterised by the very best seed yield, starting in step one of the method (as in comparison with the 8 h_5 min and eight h_15 min variants).
So far as the variant with 6 h of drying is anxious (Fig. 4c), on common approx. 46% of all extracted seeds had been obtained in step one, 24% within the second step, 15% within the third step, approx. 11% within the fourth step, about 4% within the fifth step.
When extracting seeds from larch cones, scale deflection and the variety of obtained seeds will not be assessed through the course of, as is the case with pine and spruce cones as a result of difficulties attributable to the aforementioned morphology of larch cones (Tyszkiewicz, 1949). The introduced diagrams present {that a} passable seed yield (60%) was obtained in variants with 8 and 6 h of drying already after 10 h of efficient extraction time.
The seed yield coefficient, α (3), and the cone mass yield coefficient, β (4), for every extraction variant are introduced in Desk 8.
The seed yield coefficient was the very best for variants 2 (0.73) and three (0.72), and the bottom for variants 4 (0.65) and 6 and 9 (0.67). The cone mass yield coefficient was the very best for variant 5, and the bottom for variant 9.
Seed viability
Desk 9 presents germination vitality (E) and capability (Z) for the management seeds in addition to for seeds obtained from the varied steps of the 9 course of variants, in addition to their corresponding high quality courses.
Germination vitality and capability for the management pattern had been 45% and 57%, respectively, that means that naturally launched seeds, not subjected to any thermal or mechanical therapies, had been categorized in high quality class I18. Importantly, seeds obtained from all of the studied course of variants had been additionally positioned in the identical class; their germination vitality ranged from 30 to 59%, and their germination capability from 35 to 61%. When analyzing every extraction step individually, no correlation was discovered between reducing germination vitality and successive steps. Nonetheless, the common germination vitality was 46% for seeds obtained within the first extraction step of all 9 variants, 45% for these from the second and third steps, 41% for seeds from the fourth step and 40% for these from the fifth one. Thus, in every subsequent step the common germination vitality of seeds was equal or decrease than within the earlier step, which is per literature reviews that extended drying could scale back the standard of seeds8. That is additionally corroborated by the truth that the very best germination vitality and capability was revealed by seeds from variants with 6 h of drying whereas the bottom germination indicators characterised seeds from the ten h variants. Moreover, seeds from variant 1 exhibited the bottom germination vitality and capability and seeds from variant 8–the very best.
Another excuse for the upper high quality of seeds from variants with 6 h of drying often is the decrease preliminary moisture content material of the cones as a result of longer time they had been stored at room temperature instantly earlier than the take a look at (u01 = 0.391 ({mathrm{kg}}_{mathrm{water}}cdot {mathrm{kg}}_{d.mathrm{w}.}^{-1}) as in comparison with u01 = 0.411 ({mathrm{kg}}_{mathrm{water}}cdot {mathrm{kg}}_{d.mathrm{w}.}^{-1}) for seeds from variants with 8 and 10 h of drying). These outcomes are according to the research of Tyszkiewicz8, who famous that beneath the identical temperature and humidity situations, the standard of seeds from cones with a decrease moisture content material didn’t deteriorate, in distinction to the standard of seeds obtained from cones with the next moisture content material.
The germination capability of seeds calculated from the imply capability of seeds obtained from the identical extraction steps of all course of variants was related at 45% for every of the steps.
In abstract, within the research the authors investigated a five-step technique of extracting seeds from larch cones involving immersion and warmth remedy to maximise seed yield. It was discovered that the two-step course of extensively utilized in extractories is inadequate, whereas a four-step course of doesn’t result in a considerably greater variety of obtained seeds. Thus, a three-step course of seems to be optimum.
[ad_2]
Source_link